There are many components involved in running a secure network. It’s very easy to get bogged down by different terminology and be confused about what exactly each component does. This is especially true in regards to 802.1X. 62% of breaches involve the use of stolen credentials, brute force, or phishing, and 802.1X is the best defense against these kinds of attacks. While it is incredibly secure, there are a lot of moving parts.
SecureW2 offers a turnkey EAP-TLS solution that includes JoinNow 802.1X device onboarding software, Managed PKI Services, and a Cloud RADIUS Server. Plus, deployment is a snap, just see what one of our customers said here.
RADIUS, TLS, and EAP-TLS all work in conjunction with each other in an 802.1X environment. While each function sounds similar, they each perform their own distinct function. In this article, we’re going to compare and contrast each term.
What is a RADIUS Server?
The on-premise or Cloud RADIUS servers act as the “security guard” of the network; as users connect to the network, the RADIUS authenticates their identity and authorizes them for network use. A user becomes authorized for network access after enrolling for a certificate from the PKI (Private Key Infrastructure) or confirming their credentials. Each time the user connects, the RADIUS confirms they have the correct certificate or credentials and prevents any unapproved users from accessing the network.
A key security mechanism to employ when using a RADIUS is server certificate validation. This guarantees that the user only connects to the network they intend to by configuring their device to confirm the identity of the RADIUS by checking the server certificate. If the certificate is not the one that the device is looking for, it will not send a certificate or credentials for authentication.
RADIUS servers can also be used to authenticate users from different organizations. Solutions like Eduroam have RADIUS servers that work as proxies (such as RADSEC). When a student visits a neighboring university, the unfamiliar RADIUS server can authenticate their status at their home university and grant them secure access to the neighboring university’s network.
What is EAP-TLS?
The most widely used wireless network protocols today are the Extensible Authentication Protocols (EAP) used in WPA2-Enterprise. Utilizing an EAP authentication method ensures that users’ information is sent over-the-air using encryption and avoids interception.
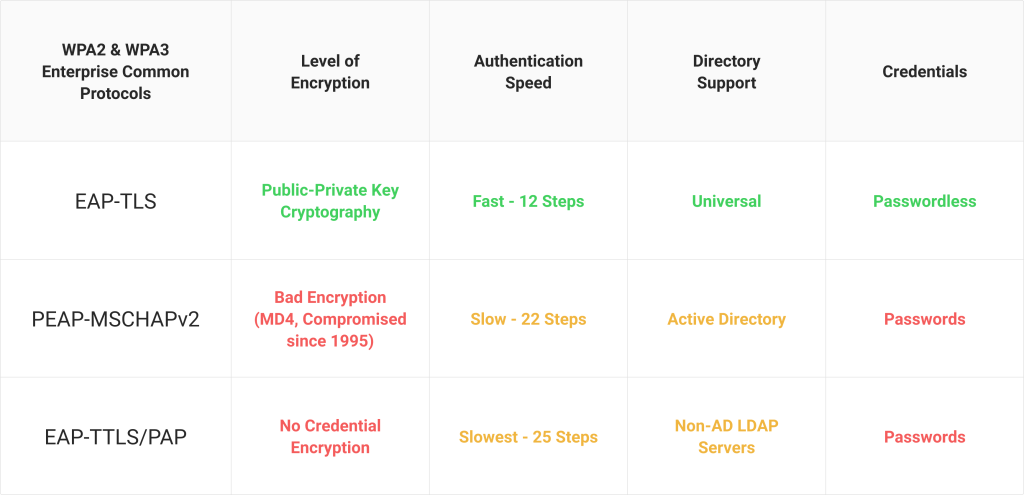
EAP-TLS is a certificate-based protocol that is widely considered one of the most secure EAP standards because it eliminates the risk of over-the-air theft. It’s also the protocol that provides the best user experience, as it eliminates password-related disconnects due to password-change policies.
What Are TLS Certificates?
Transport Layer Security (TLS) certificates are simply an upgraded version of SSL certificates. TLS certificates’ main purpose is to bind a cryptographic key to an organization’s web server to protect data transfers when someone accesses that server. It works by creating a secure connection between the two parties that allows for data to pass between the two without outside influence.
While SSL certificates are a first-of-its-kind cryptographic protocol, they are becoming less effective as the modern networking environment is favoring the more secure TLS certificate.
TLS certificates perform the same operation as SSL certificates but as a more secure and up-to-date version. They establish a secure connection between two parties, verify their identity using public-key cryptography, and prevent the interception of data by outside attackers.
A Complete Security Package With SecureW2
Many components contribute to the security and usability of a network as a complete system. If just the RADIUS authentication method is secure while the configuration of TLS certificates is left to the average network user, there is a serious risk to the integrity of the network.
SecureW2 recognizes that every facet of the wireless network must work in unison for ironclad security, so we’ve provided some turnkey concepts that every network administrator needs to consider in their network planning.
If you’re looking for the gold standard for authentication, SecureW2 offers a turnkey everything you need for a complete PKI, check out our pricing page here.