Key Points
- Choosing an effective Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) method ensures secure Wi-Fi authentication, balancing security, usability, and compatibility.
- Diverse EAP methods exist, each with varying levels of security and complexity, leading to confusion about the best choice.
- EAP-TLS offers strong security with mutual authentication, while PEAP balances security and ease of deployment.
- SecureW2 simplifies EAP-TLS with managed PKI and Cloud RADIUS solutions for easy passwordless Wi-Fi access.
Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) is a strong security layer and authentication framework used in Wi-Fi networks. It provides various methods to verify the identities of users and devices before granting access. These methods include wireless access using IEEE 802.1X, wired access using IEEE 802.1X, and Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) connections such as Virtual Private Networking (VPN). Understanding the various EAP techniques and their features will help you choose the most suitable option for protecting your wireless environment.
In this blog post, we will explore different EAP methods, address the widely available options, and help you select the right one to secure your Wi-Fi network.
What is EAP in Networking?
The Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) is a security framework that manages communication among devices, such as laptops or phones, and authenticates servers to gain access to a Wi-Fi network. It establishes a secure connection that allows only authorized devices with the right credentials to develop a connection.
How Does EAP Work in the Authentication Process?
The EAP authentication process comprises multiple essential steps and individuals, including the supplicant, the authenticator, and the authentication server, such as a RADIUS server. Here is a concise summary of the process:
- Initialization: The supplicant initiates gaining access to the network by establishing a connection with the authenticator.
- Identity Request/Response: The authenticator initiates an Identity Request/Response by sending an EAP-Request message to the supplicant and requests its identity. The supplicant replies by sending an EAP-Response message that includes its identity information.
- Method Selection and Negotiation: The authenticator transmits the identity information to the authentication server, which determines the suitable EAP method according to network policies and the capabilities of the supplicant. This step involves defining the specific authentication method that protocol triggers a sequence of message exchanges between the supplicant and the authentication server. The authenticator enables it. These exchanges authenticate the supplicant’s credentials and build mutual trust.
- Authentication Result: The authentication result is determined by the authentication server’s successful verification of the supplicant’s credentials. Upon successful authentication, the authentication server sends an EAP-Success message to the authenticator, allowing network access to the supplicant. If authentication fails, an EAP-Failure message is transmitted, which causes the denial of access to the supplicant.
This process guarantees that the client device and the network authenticate each other while providing a secure method for managing access to the network.
What are the Common EAP Methods?
Several EAP methods in the market offer security, complexity, and suitability for various use cases. Understanding how to choose the right one to secure your WiFi network is important. The following are some commonly used EAP methods:
- PEAP (Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol): PEAP uses usernames and passwords for authentication and adds an additional security layer by encrypting communication between the device and server. Vulnerability can occur if server certificate validation isn’t configured properly for all devices.
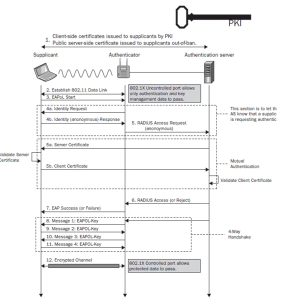
- EAP-TLS (Extensible Authentication Protocol-Transport Layer Security): This transport layer security method relies on digital certificates for authentication and offers a robust security posture compared to username/password methods. In EAP-TLS, both the device and the server show certificates. This ensures mutual authentication and strong encryption.
- TTLS (Tunneled TLS): Like PEAP, Tunneled Transport Layer Security or TTLS employs a tunnel to secure communication. Still, it provides more flexibility regarding the authentication method applied within the tunnel. The authentication process can involve various methods such as username/password, certificates, or other methods.
- LEAP (Lightweight Extensible Authentication Protocol): The Lightweight Extensible Authentication Protocol (LEAP) is a proprietary authentication method developed by Cisco. It relies on usernames and passwords for the authentication. Although it provides a certain level of security, it does not qualify as highly resilient as other EAP protocols due to possible vulnerabilities.
Choosing the appropriate EAP method relies on your network security requirements, including security needed, ease of deployment, and compatibility with existing infrastructure. Although PEAP is commonly utilized because it combines security and ease of implementation, it is essential to ensure the validation of server certificates to prevent vulnerabilities. On the other hand, EAP-TLS offers the highest level of security and is recommended for scenarios where security is required. Sufficient resources are available to manage the complexity of digital certificates.
EAP Method Comparison: Security, Ease of Use, and Scalability
When selecting the right EAP protocol for your needs, you need to balance security, ease of use, and the ability to grow. The following table shows some common authentication methods:

Security Level
- EAP-TLS is recognized for its exceptional level of security. It employs mutual authentication, wherein the device and the server authenticate using digital certificates. This greatly reduces unauthorized access compared to username/password techniques.
- PEAP can provide a high level of security when the validation of server certificates is correctly configured. However, ignoring this essential step leaves the network vulnerable to man-in-the-middle attacks.
- TTLS relies on the inner authentication method selected. Although it provides flexibility and strong security, it requires proper configuration.
- LEAP provides a minimal level of security and is not suitable for high-security environments due to known weaknesses.
Ease of Use
- PEAP and LEAP generally rely on username/password credentials and are easier to set up.
- EAP-TLS manages digital certificates on both devices, the client and the server, which makes it slightly more complex but offers a higher level of security.
- TTLS setup can vary depending on the chosen inner authentication method.
Scalability
- All these EAP authentication methods are generally scalable, and you can use them to manage many devices in an enterprise network.
Choosing the Right EAP Authentication Method
As security is the main concern for many organizations and businesses, EAP-TLS offers robust security and scalability. If user-friendliness is a major concern, PEAP with strict server certificate validation may be an option.
What EAP Method Should I Use for Wi-Fi?
Now that you understand the various EAP methods and their advantages and disadvantages, you may wonder which is best for your Wi-Fi network. Here’s a breakdown to help you choose:
- Prioritize Security: If robust security is your top concern, especially with sensitive data, then EAP-TLS is the best option. Its mutual authentication and strong encryption provide high protection against unauthorized access.
- Balance Security and Ease of Use: Consider using PEAP with strong server certificate validation to balance security and user-friendliness. This approach may be appropriate for smaller networks.
- Focus on User Convenience (Not Recommended): Emphasizing User Convenience (Not Advised): In cases where user convenience is the priority, LEAP may be a good option. However, this approach should be avoided because it has a lower level of security.
Remember that security should always be a priority when you set up your Wi-Fi network. Even though ease of use is important, strong security measures like EAP-TLS protect your data and resources.
How Does EAP Provide Fast Authentication?
Quick and efficient authentication is necessary to keep wireless networks running smoothly. EAP protocols offer strong security without slowing the network or compromising user experience during authentication. EAP enables fast authentication in the following ways:
Efficient Communication Protocols
EAP methods utilize streamlined communication protocols to minimize the time needed for the authentication process. Implementing Transport Layer Security (TLS) in protocols such as EAP-TLS, PEAP, and EAP-TTLS guarantees the quick establishment of a secure tunnel, enabling a prompt exchange of authentication data.
Session Resumption
Several EAP methods facilitate session resumption. This enables previously authenticated clients to reconnect without repeating the entire authentication process, greatly decreasing the time required for subsequent connections. For instance, in protocols such as EAP-TLS and PEAP, TLS session resumption enables clients to quickly resume sessions with minimal additional data, speeding up the authentication process.
Pre-Authentication
Some EAP methods support pre-authentication, where the client device can authenticate to the network before using network resources. This means the authentication is already completed before the device connects. Pre-authentication is particularly useful in environments with high mobility, such as campuses or large enterprise networks.
Lightweight Inner Authentication
EAP methods like EAP-TTLS and PEAP use lightweight inner authentication protocols within the secure TLS tunnel. This approach reduces the complexity and time required for the authentication process while maintaining security. For instance, using MS-CHAPv2 within PEAP allows quick and efficient credential verification.
Caching Mechanisms
EAP methods can utilize caching mechanisms to store authentication credentials and session information. This reduces the need to verify credentials repeatedly for the same user or device and speeds up the authentication process for returning users. Cached credentials can be securely stored and managed to ensure the authentication process remains fast and secure.
Importance of Comprehensive Onboarding Solutions
EAP methods establish a foundation for reliable and fast authentication. Implementing comprehensive onboarding solutions can greatly improve overall efficiency and user satisfaction. These solutions utilize automation and optimization techniques to simplify the setup and control of EAP settings. This guarantees that devices are authenticated correctly without the user’s involvement.
Automated Certificate Management
Onboarding solutions that support automated certificate management make it easier to set up EAP-TLS by issuing, renewing, and revoking digital certificates. This simplifies administration and ensures that devices always have valid certificates for authentication.
Policy Enforcement and Monitoring
Comprehensive onboarding solutions also enable network administrators to implement security policies and monitor authentication activities. This guarantees that all devices adhere to the organization’s security standards. Real-time monitoring enables administrators to detect and resolve potential problems promptly and ensure the network’s overall health and performance.
What is EAP Used For?
The Extensible Authentication Protocol is a flexible framework used in different networking scenarios to ensure secure authentication. Its ability to accommodate various authentication methods guarantees the safety and reliability of network access. The following are the main uses of EAP in networking:
Securing WiFi Networks
EAP methods offer the essential structure for verifying the identities of users and devices attempting to establish connections with wireless networks. It ensures that only authorized entities are granted access.
- Enterprise WiFi: Enterprise WiFi networks in corporate environments commonly utilize the Extensible Authentication Protocol to implement stringent access controls using EAP-TLS or PEAP protocols. These authentication methods ensure that employees and devices experience proper authentication before accessing sensitive corporate resources.
- Educational Institutions: Educational institutions such as universities and colleges implement EAP authentication to ensure the security of their campus-wide WiFi networks. This enables students and staff to connect to academic resources and the internet securely.
- Public Hotspots: WiFi hotspots use EAP authentication to establish a secure connection and protect users’ data against potential security risks.
VPN Authentication
EAP authentication is also used in Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) to authenticate users and devices before granting them access to the secure VPN tunnel. This ensures that only authorized users can connect to the VPN to protect the network from unauthorized access and potential security breaches.
- Remote Access VPNs: Remote Access VPNs utilize EAP methods such as EAP-TLS to securely authenticate remote workers connecting to the corporate network from distant locations.
- Site-to-Site VPNs: Extensible Authentication Protocol is used in site-to-site VPNs to ensure the security of connections between various corporate locations. It ensures that the data being transmitted remains confidential and maintains its integrity.
Network Access Control (NAC)
Network Access Control systems utilize the Extensible Authentication Protocol to enforce and maintain security policies for devices that establish a connection with the network. Integrating EAP with NAC solutions allows organizations to guarantee secure access to the devices while improving network security.
- Endpoint Compliance: The organization utilizes EAP to authenticate devices based on compliance with security policies. This includes requirements such as having current antivirus software and up-to-date operating system patches. Only devices that meet these criteria are granted network access.
- Guest Access: NAC solutions utilize the Extensible Authentication Protocol to grant secure access to guests on the network. This guarantees that they can connect without jeopardizing the corporate network’s security.
3G and 4G Mobile Networks
In mobile networks, EAP-SIM and EAP-AKA authenticate users by leveraging their SIM cards. This offers a reliable and smooth method for mobile devices to connect to the network and utilize the current mobile infrastructure for authentication.
- Subscriber Authentication: EAP-SIM and EAP-AKA authenticate users by verifying the credentials stored on their SIM cards. This ensures that only authorized subscribers can connect to the mobile network.
- Seamless Roaming: These EAP methods enable seamless roaming between different mobile networks and provide users with uninterrupted connectivity as they move.
Importance of EAP in Network Security
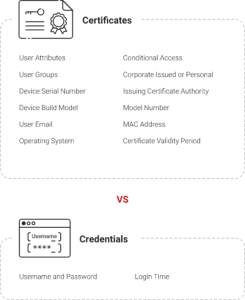
EAP authentication ensures that only authorized users and devices can access network resources. This is critical for preventing unauthorized access to protect sensitive data and ensure network integrity.
- Data Protection: EAP methods help protect data by ensuring that only authenticated devices can access the network. This reduces the risk of data breaches and unauthorized data access.
- Network Integrity: EAP authentication ensures the integrity of the network by implementing strong authentication procedures. This prevents unauthorized devices from compromising network security.
- User Trust: The implementation of robust authentication methods through EAP fosters confidence in users and ensures the security of their data and connections.
EAP is essential in securing various types of networks, from WiFi and VPNs to mobile networks and NAC systems. Its ability to support multiple authentication methods makes it adaptable to different security needs.
Choosing the Right EAP Method
Understanding the various EAP methods and their practical uses is essential to choose the most suitable one for your network. Now, let us examine some of the most effective EAP techniques and their specific applications.
EAP-TLS: The Best EAP Method
EAP-TLS is the best EAP method due to its robust security features. It uses mutual authentication and strong encryption, making it highly resistant to attacks. This method provides a high level of security for network authentication.
Default EAP Method
There isn’t a single default EAP method, as it varies based on network configurations. However, PEAP is commonly used because it offers a good balance between security and ease of deployment.
Connecting to Wi-Fi Using EAP Methods
Configuring your devices to connect to Wi-Fi using different EAP methods can enhance your network’s security. Here’s how to connect using various EAP methods:
Steps to Connect to Wi-Fi Using EAP Methods
To connect to Wi-Fi using an EAP method, select the network, choose the appropriate EAP method (e.g., EAP-TLS, PEAP), and enter the required credentials, such as a username and password or a digital certificate. This setup ensures secure authentication and access to the network.
Connecting to EAP WiFi
To connect to an EAP WiFi network:
- Select the network from the available WiFi options.
- Configure the appropriate EAP settings (e.g., EAP-TLS, PEAP).
- Provide the necessary authentication credentials, such as a certificate, username, and password.
- Ensure the device validates the server certificate if methods like PEAP are used to prevent vulnerabilities.
Differences Between PEAP and EAP-FAST
PEAP uses a secure TLS tunnel to protect the inner authentication, often using MS-CHAPv2. On the other hand, EAP-FAST (Flexible Authentication via Secure Tunneling) uses a Protected Access Credential (PAC) to establish a secure tunnel, providing faster and more efficient authentication. Understanding these differences helps choose the right method based on security needs and deployment complexity.
Role of EAP in Network Devices and Infrastructure
EAP plays an important role in securing various network devices and infrastructure components. Explore how EAP integrates with routers, access points, and other network devices.
EAP in Routers
EAP in a router refers to the router’s support for the Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP). This enables it to handle various EAP methods for secure authentication of devices connecting to the network, essential for maintaining a secure and reliable network environment.
EAP Devices
EAP devices include access points, routers, and client devices that support the Extensible Authentication Protocol for secure network authentication. These devices are key to implementing EAP methods and ensuring secure access to the network.
The Best Choice: EAP-TLS with Secure Onboarding
Undoubtedly, EAP-TLS is the most reliable choice for ensuring the security of Wi-Fi networks. It provides:
Robust Security with Mutual Authentication
EAP-TLS stands out due to its use of mutual authentication. The client and the server must present and verify each other’s digital certificates, eliminating the risk of unauthorized access. This process ensures that only devices with valid certificates can access the network, providing a robust defense against man-in-the-middle attacks and other security threats.
The mutual authentication mechanism is a fundamental part of the protocol, making it extremely difficult for attackers to impersonate either party.
Strong Encryption and Data Protection
One of the key strengths of EAP-TLS is its reliance on strong encryption. The protocol uses advanced cryptographic techniques to encrypt data during transmission, protecting sensitive information from eavesdropping and interception. This encryption secures the authentication process and ensures that all subsequent data exchanges between the client and the server are protected.
The use of public key cryptography, specifically elliptic curve cryptography (ECC), enhances the security of the protocol, making it highly resistant to various forms of network intrusion.
Enhanced User Experience and Reduced Administrative Overhead
EAP-TLS offers a seamless user experience by eliminating the need for passwords, which are prone to being forgotten, reused, or stolen. Instead, it utilizes digital certificates that can be automatically enrolled and managed. This reduces the administrative overhead associated with password resets and management, freeing up IT resources and improving overall network efficiency.
EAP-TLS provides users with effortless authentication whenever their device is within the network’s coverage area, streamlining the connection process and enhancing efficiency.
Comprehensive Network Visibility and Access Control
Using EAP-TLS improves network visibility and access control by binding digital certificates to individual users or devices. This ensures that only authenticated devices with valid certificates can access the network, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Administrators can easily track and manage network access, ensuring that security policies are consistently enforced. This capability enhances the organization’s overall security posture, making it easier to identify and mitigate potential security threats.
Our Solution: Simplifying Secure Onboarding with EAP-TLS
Our PKI and Cloud RADIUS solution offers a streamlined approach to implementing and managing EAP-TLS:
- Simplified PKI Management: We take care of the complex PKI infrastructure and allow you to easily issue and manage digital certificates for your devices and servers.
- Seamless Cloud RADIUS Deployment: Our Cloud RADIUS service centralizes user authentication and eliminates the need for on-premises RADIUS servers.
- Automated Certificate Enrollment: Devices can automatically enroll, obtain the necessary certificates, and streamline the onboarding process for users.
By leveraging our solution, you can:
- Enjoy the robust security of EAP-TLS without the administrative burden.
- Simplify user onboarding with automated certificate management.
- Scale your network securely as your organization grows.
Ready to Secure Your Wi-Fi with EAP-TLS?
The Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) provides a robust framework for securing Wi-Fi networks and offers various methods to authenticate users and devices. By understanding the different EAP methods—such as EAP-TLS, PEAP, and EAP-TTLS—network administrators can select the most appropriate one for their specific needs. EAP-TLS’s use of mutual authentication and strong encryption makes it stand out as the best choice for high-security environments.
Moreover, integrating EAP methods with automated certificate management and policy enforcement can significantly enhance the security and efficiency of the authentication process. These solutions streamline EAP-TLS deployment by simplifying the configuration of digital certificates, reducing administrative overhead, and ensuring consistent application of security policies. As organizations prioritize network security, adopting EAP-TLS can provide a secure, scalable, and user-friendly authentication framework, safeguarding sensitive data and maintaining network integrity.
Refrain from settling for compromises between security and convenience. Explore our PKI and Cloud RADIUS solutions. Our team of experts can help you navigate the transition to secure EAP-TLS authentication and ensure your Wi-Fi network remains protected from unauthorized access.