Key Points
- The sophistication of cyberattacks has rendered traditional encryption methods vulnerable, necessitating advancements like SHA-2 for collision resistance and ECC for efficient encryption.
- SHA-2 and ECC are pivotal cryptographic technologies that enhance encryption, authentication, and integrity in digital certificates, ensuring secure communication.
- SHA-2's robust hashing algorithms verify data integrity, while ECC provides efficient key generation and encryption, offering scalable, high-performance security solutions.
- SecureW2’s managed PKI supports SHA-2, ECC, and other algorithms, automating certificate management for secure, scalable deployments.
Cryptographic systems are at the heart of digital certificates, enabling encryption, authentication, and integrity. SHA-2 and ECC are two pivotal technologies that protect everything from SSL certificates to system integrity checks. These tools act as digital shields, ensuring private communication over public networks. This article is an in-depth comparison of these two encryption algorithms – what they mean, how they work, and what the differences are.
What Is Secure Hash Algorithm 2 (SHA-2)?
SHA-2 is a family of cryptographic hash functions designed by the National Security Agency (NSA) and standardized by NIST. It is widely used in digital certificates, SSL/TLS encryption, and data integrity verification. Unlike its predecessor, SHA-1, SHA-2 is highly resistant to collision attacks, making it a cornerstone of modern cryptographic practices. SHA-2 includes multiple hash functions, such as SHA-224, SHA-256, SHA-384, and SHA-512, differentiated by their bit lengths, which dictate the size of the resulting hash value. Applications of SHA-2 include digital signatures, authentication, and SSL/TLS encryption.
Core Features of SHA-2 Certificates
SHA-2 certificates incorporate several features that enhance data integrity, resistance to attacks, and compatibility across platforms, making them indispensable for secure communications and authentication. Below, we explore the key attributes that set SHA-2 apart as a trusted cryptographic standard:
Hashing Algorithm Variants
SHA-2 supports multiple hashing algorithm variants, including SHA-256, SHA-384, and SHA-512, differentiated by their bit lengths. This flexibility allows organizations to select an appropriate variant based on their security and performance needs. For instance, SHA-256 provides an optimal balance of computational efficiency and robustness, while SHA-512 offers higher security for sensitive applications.
Collision Resistance
One of SHA-2’s most critical attributes is its resistance to collision attacks, where two different inputs produce the same hash. The algorithm’s intricate mathematical structure significantly reduces the likelihood of such occurrences, ensuring data integrity and making it reliable for applications like digital signatures and certificate authentication.
Fixed Hash Size
SHA-2 generates a consistent hash length regardless of the input size, ensuring predictability and uniformity in cryptographic processes. This fixed-size hash is crucial for verifying the integrity of data, such as in hashing passwords or validating SSL certificates.
Enhanced Security
Compared to its predecessor, SHA-1, SHA-2 employs a more complex mathematical function, making it exponentially harder to exploit. This enhanced security makes it a primary algorithm for sensitive tasks like secure messaging, data storage, and digital certificates.
Wide Compatibility
SHA-2 is widely supported across contemporary systems, browsers, and applications, including Google Chrome and Microsoft Windows. This compatibility ensures seamless deployment across diverse environments, making it a trusted standard for certificate authorities and enterprises globally.
Cryptographic Hash Function Image source: Remitano.com
How SHA-2 Works
SHA-2 operates as a cryptographic hash function, converting variable-length input data into a fixed-size hash value. The process involves breaking input data into blocks, padding it to meet size requirements, and applying iterative compression using logical operations like bitwise shifts, XOR, and modular addition. The resulting output—a fixed-length hash value—serves as a unique digital fingerprint of the input data. SHA-2 is deterministic, meaning the same input consistently produces the same output, ensuring data integrity and authenticity.
The Role of Cryptographic Hash Functions in SHA-2
Cryptographic hash functions like SHA-2 condense data into a fixed-size hash. SHA-2 uses a hashing algorithm resistant to collision attacks, where two inputs produce the same hash. It processes data through multiple rounds of transformations, ensuring irreversible outputs. This property is crucial for verifying digital signatures, storing passwords securely, and preventing unauthorized data tampering.
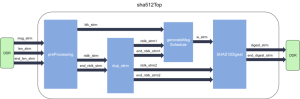
The internal structure of SHA-2 algorithms Image Source: xilinx.github.io
What are SHA-224, SHA-256, SHA-384, and SHA-512?
SHA-2 includes six hash functions distinguished by their output lengths:
- SHA-224: Produces a 224-bit hash, ideal for constrained environments.
- SHA-256: A widely-used, secure hashing standard with a 256-bit output.
- SHA-384 and SHA-512: These provide stronger security by producing longer hashes, suited for high-security use cases like digital certificates.
The Role of Certificate Authorities in SHA-2-Based Certificates
Certificate Authorities (CAs) play a pivotal role in implementing SHA-2 in digital certificates. By leveraging SHA-2’s cryptographic hash function, a certificate authority ensures the integrity of certificate data, generating a digital signature that validates the certificate’s authenticity. When issuing a legitimate certificate, the CA signs it using a private key, creating a secure digital signature that the recipient can verify against the CA’s public key.
This process guarantees that the certificate has not been altered or replaced with a fraudulent certificate during transmission. The hash function ensures any tampering with the original data results in a completely different hash, making illegitimate modifications easily detectable.
CAs also rely on SHA-2 to maintain trust in their certificate hierarchies, ensuring that all issued certificates adhere to stringent integrity and security standards. This approach prevents misuse and reinforces the authenticity of secure communications across networks and systems. By integrating SHA-2, CAs enhance the reliability of digital certificates, safeguarding sensitive transactions and communications.
What is Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC)?
ECC is a public-key encryption algorithm based on the mathematical principles of elliptic curves over finite fields. ECC provides equivalent security to traditional RSA cryptography but with significantly smaller key sizes, improving efficiency and reducing computational load. For instance, a 256-bit ECC key offers comparable security to a 3072-bit RSA key, making it ideal for devices with limited processing power. ECC certificates leverage the elliptic curve discrete logarithm problem (ECDLP), a complex problem that ensures data confidentiality and resistance to cryptographic attacks.
Key advantages of ECC include faster key generation, reduced storage requirements, and lower energy consumption, which makes ECC well-suited for IoT, mobile devices, and large-scale systems. In practice, ECC secures SSL/TLS connections, provides robust digital signatures, and enhances encryption in systems like secure messaging and financial transactions. ECC’s efficiency and strength ensure scalability, especially in high-traffic or resource-constrained environments, supporting modern digital security demands.
How ECC Works
Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) operates by leveraging the mathematical properties of elliptic curves over finite fields to establish secure cryptographic operations. At its core, ECC utilizes the elliptic curve equation y² = x³ + ax + b mod p, where a and b define the curve’s structure. The points on this curve, combined with modular arithmetic, enable operations like point addition and scalar multiplication, forming the foundation for ECC’s cryptographic strength.
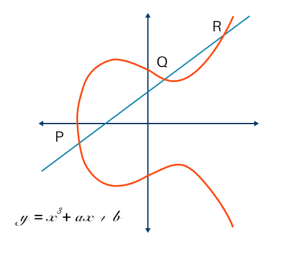
The elliptical curve
Elliptic Curve Theory in Cryptography
ECC’s security relies on the elliptic curve discrete logarithm problem (ECDLP), which is computationally infeasible to reverse within practical timeframes. Unlike traditional algorithms, such as RSA, which depend on integer factorization, ECC achieves higher security with shorter key lengths. This reduces computational overhead while maintaining robust encryption.
Key Generation and Verification Processes in ECC
ECC key generation begins by selecting a base point on the curve, then multiplying it by a randomly chosen private key to produce a public key. The private key remains confidential, while the public key facilitates secure encryption and digital signature verification. Verification involves elliptic curve point operations, ensuring message integrity and authenticity without exposing private keys.
Why ECC Certificates Are Considered Efficient
ECC certificates minimize resource consumption due to shorter key lengths and faster cryptographic operations. This efficiency supports high-traffic environments, low-power IoT devices, and modern systems requiring scalable encryption. Its compact size and computational speed make ECC optimal for securing SSL certificates and safeguarding data in constrained or high-demand scenarios.
Comparing Performance: SHA-2 vs. ECC
The performance of SHA-2 and ECC differs fundamentally due to their distinct cryptographic roles:
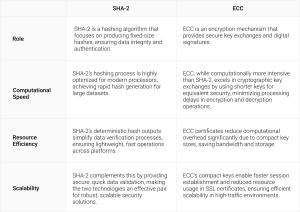
Security Strength: SHA-2 vs ECC
The cryptographic security of SHA-2 and ECC lies in their resistance to attacks and ability to ensure data protection. While SHA-2 is a secure hashing algorithm, ECC offers enhanced encryption strength. Each has unique properties that bolster their reliability in securing modern digital systems.
Resistance to Common Cryptographic Attacks
SHA-2 is designed to resist collision attacks, where two different inputs produce the same hash value, through its robust cryptographic structure and varying bit lengths (e.g., SHA-256 and SHA-512). ECC, on the other hand, secures key exchanges by leveraging the elliptic curve discrete logarithm problem (ECDLP), a computationally hard problem that withstands conventional attack vectors, including replay and man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks.
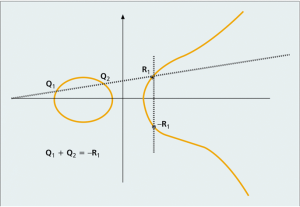
Elliptic Curve Discrete Logarithm Problem Image Source: ResearchGate
Quantum Computing Threats to SHA-2 and ECC
Quantum computing poses significant risks to cryptographic systems. Shor’s algorithm threatens ECC’s ECDLP, potentially compromising its private key security. SHA-2, while not inherently quantum-safe, is less affected as quantum algorithms like Grover’s primarily reduce brute force efficiency, necessitating increased hash lengths (e.g., transitioning from SHA-256 to SHA-512).
Why ECC is More Resistant to Brute Force Attacks
ECC’s compact key sizes are inherently secure against brute force due to their reliance on ECDLP. A 256-bit ECC key offers the same strength as a 3072-bit RSA key, significantly narrowing the attack surface. Its efficiency and scalability ensure robust protection even against sophisticated adversaries.
Compatibility and Interoperability
The implementation of SHA-2 and ECC in cryptographic systems depends heavily on their compatibility with existing platforms and their ability to interoperate seamlessly. While both are widely adopted, their integration often reveals differing levels of platform support and deployment challenges.
SHA-2 Certificate Compatibility Across Platforms
SHA-2 certificates enjoy extensive compatibility across modern systems and applications. After the depreciation of SHA-1 due to its vulnerability to collision attacks, SHA-2 has become the standard for digital certificates, supported by all major operating systems, browsers like Google Chrome, and SSL certificates. Its universal adoption ensures smooth integration with web browsers, certificate authorities, and security protocols without additional configuration.
Challenges of Deploying ECC Certificates in Legacy Systems
While ECC certificates are increasingly favored for their efficiency and security, legacy systems often lack support for elliptic curve algorithms. Outdated platforms and devices may struggle to process ECC keys, necessitating additional software updates or hardware replacements to ensure compatibility. This challenge underscores the importance of ECC readiness in environments reliant on older infrastructure, especially when transitioning from RSA-based systems.
Ensuring Integrity and Trust: SHA-2 and ECC in Digital Certificates
The roles of SHA-2 and ECC in digital certificates extend beyond encryption and authentication; they are critical in ensuring data integrity and trust in modern digital communication. Both cryptographic standards address the challenges of safeguarding against fraudulent certificates and preserving the authenticity of legitimate certificates.
Integrity Through Hash Calculation and Hash Algorithms
SHA-2 employs hashing algorithms to condense data from the original message into a fixed-size hash value. This process creates a unique fingerprint of the input, ensuring any tampering generates a completely different hash. This capability is vital for applications like digital signatures, where the hash calculation guarantees that the original data has not been altered.
ECC’s Role in Signing Legitimate Certificates
ECC secures digital certificates through its robust key pair system. The primary algorithm behind ECC enables efficient generation of secure private keys while ensuring small bit lengths. This efficiency aids in verifying the legitimacy of certificates and detecting any fraudulent certificates. By combining ECC’s efficient key generation with SHA-2’s integrity checks, systems achieve a comprehensive security framework adaptable to diverse use cases.
SecureW2’s Managed PKI For Certificate Deployment
SecureW2’s JoinNow Dynamic PKI delivers an advanced, fully managed solution for organizations seeking secure, scalable, and efficient digital certificate management. By leveraging modern encryption algorithms like ECC, RSA 2048, RSA 4096, and SHA-256, our PKI ensures robust security while maintaining compatibility with a wide range of systems and devices.
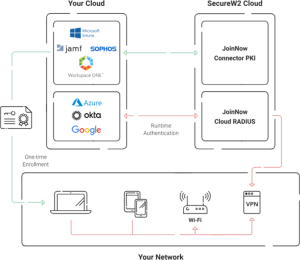
At the core of SecureW2’s PKI is a suite of hashing algorithms that condense data into unique digital fingerprints, enabling reliable integrity checks. Our solutions perform hash calculations with precision, ensuring that even minor alterations to original data result in entirely different hashes, safeguarding against tampering and fraudulent certificates. The primary algorithm driving our PKI ensures efficient generation of secure key pairs for digital signatures, allowing organizations to issue legitimate certificates that meet the highest security standards. These certificates integrate seamlessly into modern IT infrastructures, supporting use cases such as secure Wi-Fi authentication, encrypted communications, and device provisioning.
SecureW2’s managed PKI eliminates the administrative burden of maintaining a public key infrastructure in-house. With automation for certificate issuance, renewal, and revocation, it minimizes errors and enhances operational efficiency. Our service is built to scale, catering to environments ranging from small businesses to enterprise-level deployments, and comes at an affordable price.