LDAP and SAML are major authentication protocols that securely authenticate users to a network. They determine how users interact with a resource by connecting them to the respective directory services, like an on-premise or a cloud-based directory.
The Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) is an open standard protocol created in the late 1990s. It is popularly used to date to access many resources and applications by connecting to a directory service like Active Directory. The Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) was created in the early 2000s and is an assertion-based authentication protocol that federates identities to web applications and directories.
As more and more organizations consider moving infrastructure to the cloud, understanding the protocols that make this possible is critical. Let’s dive deep into the LDAP and SAML protocols, their features and similarities, and how to leverage them to secure your network effectively.
What is The Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) and Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) Protocol?
While the LDAP and the SAML protocol sound similar, they are separate methods for securely authenticating users to a network. Each protocol controls user authentication to a resource in different ways. Let’s look at SAML and LDAP individually.
The LDAP Protocol
The LDAP protocol has many use cases, but one of its most common is user authentication. It can connect authentication servers, such as RADIUS servers, to on-premise directories like Microsoft’s Active Directory. As a result, users can have their identity confirmed and quickly access on-premise servers.
The LDAP server uses a dictionary service like the Active Directory to authenticate a user’s credentials. Upon a service request by a user, the protocol checks with the credentials stored in the directory and provides user access based on pre-defined authorization. Thus, LDAP acts as a double authenticator.
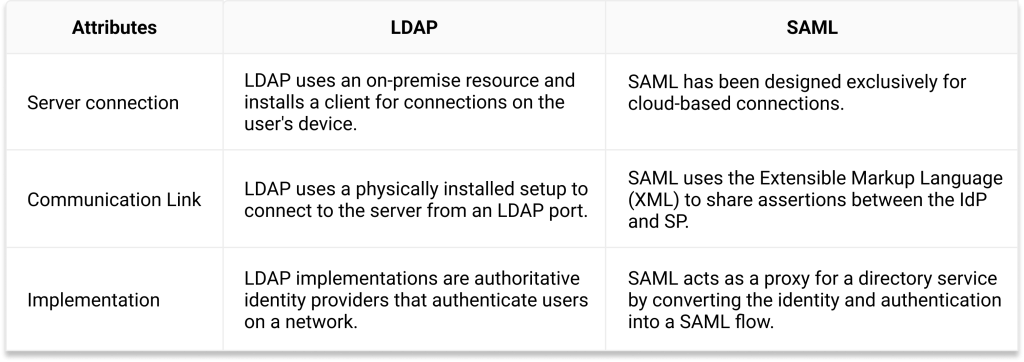
It has proven to be highly effective in communicating with on-premise servers and protecting users’ identities and data, but the on-premise aspect of LDAP is its main weakness. LDAP must be physically installed because it works in conjunction with servers on-site. This includes a more labor-intensive setup process and higher management costs over time.
The SAML Protocol
SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) was created primarily to modernize authentication and adapt to the growing cloud-based networking trend.
SAML connects the RADIUS to (typically cloud) directories to authenticate users for any service that supports it – VPN, web applications, Wi-Fi, and more.
SAML facilitates the exchange of information between an identity provider (IdP) and a service provider (SP) to communicate with each other and complete the authentication process. A user typically requests a service from a service provider, and the service provider requests an authentication from the identity provider (IdP).
SAML makes it easier by requiring the user to sign in to the service with a single set of credentials, thus enabling SAML SSO verification.
Similarities between SAML vs LDAP
Both SAML and LDAP use a similar identity and authentication process to authenticate users and give them access to organizational resources. They do this by communicating with an identity provider (either cloud-based or on-premise) and establishing authentication with an application or service.
SAML and LDAP also work by establishing SSO verification as per the directory service configuration. They are used for authorization and authentication. However, they cannot account for users on a network.
The Differences between the LDAP Authentication Protocol vs SAML Authentication Protocol
As stated above, LDAP was built for on-site authentication, while SAML was built to communicate with cloud-based servers and applications. Both bring advantages and disadvantages and present very different methods of securing the authentication process.
Use cases for LDAP vs SAML
LDAP works well for organizations with on-premise setups and gives an organization more control over authentication and authorization. SAML can extend user identity from a directory to a host of web-based applications to enable SSO. Let us look at some use cases for LDAP and SAML below:
- LDAP and SAML provide secure access management for users to access data, files, devices, and applications for their day-to-day work.
- They provide a secure authentication method for users before they are granted system access.
- They facilitate communication channels between systems and applications and directory services, IdPs, and SPs.
- They help enable secure single sign-on and enhance user experience by enabling a single set of credentials to access multiple resources.
Azure Authentication with LDAP vs SAML
Microsoft’s Active Directory (AD) has become a commonly used identity provider. Azure AD is an upgrade to AD to allow for greater flexibility with cloud-based authentication. As a result, the LDAP authentication server does not support Azure AD. An LDAP server can be configured to work with Azure AD (Microsoft Entra ID) when Azure AD Domain Services are added, but this is a separate product that needs to be purchased and configured on top of Azure AD.
On the other hand, SAML is a cloud-based access protocol and, therefore, is easily configured to communicate with Azure AD. SAML can be configured to communicate with applications, servers, etc., and Azure AD securely connects users to the necessary resources. It can also be utilized to configure an SSO-based network authentication setup. Microsoft provides a link demonstrating how SAML and Azure AD can be configured to work together.
Use LDAP and SAML with SecureW2
SecureW2’s Cloud RADIUS allows organizations to authenticate users for VPN, Wi-Fi, web applications, email security, and more. When working in concert with Azure AD and SAML, your IT team can rest assured that users are securely authenticated to the network.
The latest improvement to RADIUS developed by SecureW2 is Dynamic RADIUS, which allows for more complex communication with the IDP during authentication. Traditionally, the IDP is not communicated during authentication; a certificate is presented and determined to be legitimate based on public key cryptography and the CRL.
Dynamic RADIUS allows for direct communication with the IDP via SAML. This enables real-time directory editing when a user’s status changes within an organization. Instead of replacing all their certificates on all their devices, they can simply update their permissions within the IDP in real-time.
While SAML and LDAP are both viable access protocols and are still widely used, it’s clear to see which is better adapted for viability in the future. As more technology moves to the cloud, LDAP will be left behind and phased out of most organizations. In the meantime, SecureW2 can still accommodate LDAP, even operating it in unison with SAML.
Check out SecureW2’s pricing page to see if our certificate solutions utilizing SAML fit your organization’s plan.