MAC Authentication Bypass (MAB) is an access control protocol that allows access using a machine’s MAC address (Media Access Control Address). It is port-based access control that can be enabled or disabled dynamically on the basis of a device’s MAC address. Not considered the most secure authentication method, it is visibility and entity-based access control that can only check the machine’s MAC address. MAC auth bypass is applied for machines that don’t support 802.1X authentication like printers, or smart speakers.
How MAC Auth Bypass Works
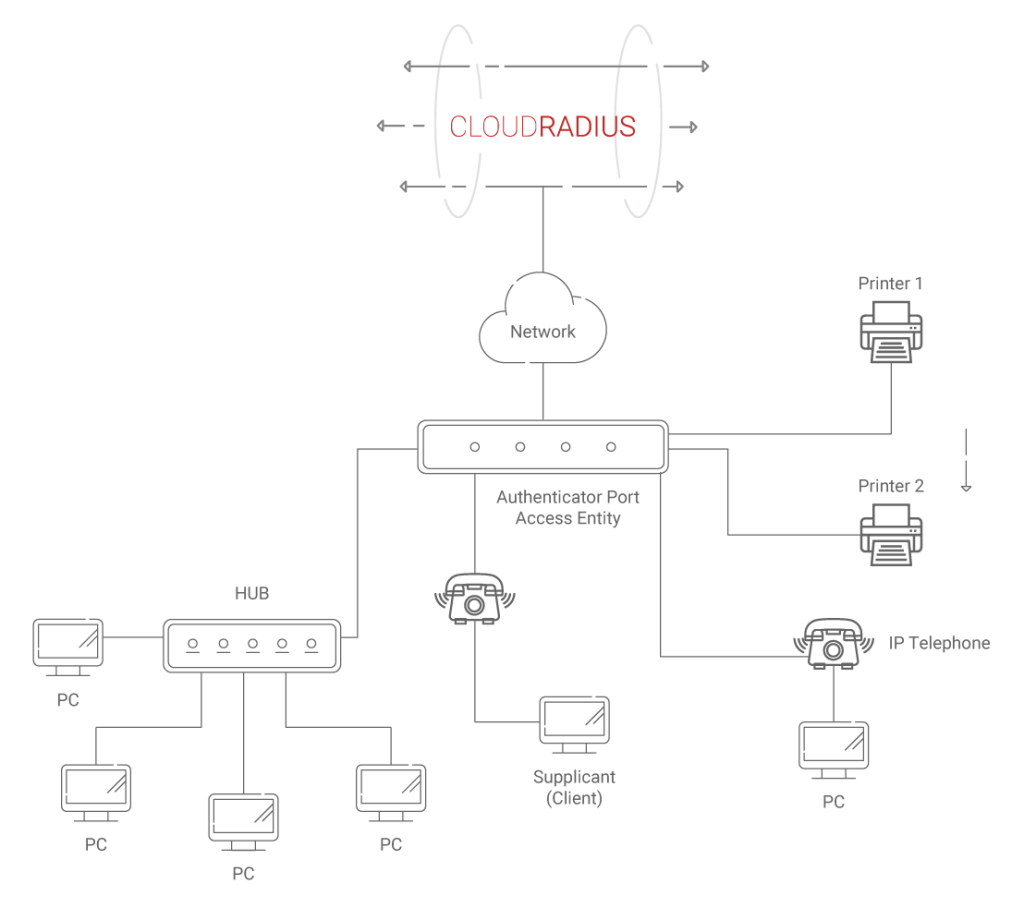
With MAB, the switch uses the MAC address database to verify the user/device identity before granting access. When RADIUS MAC auth Bypass is enabled, MAB takes 3 steps of authentication to provide device/user access.
1.Initiation
Switch submits an EAPoL identity request and every 30 seconds (by default) a message is sent to the endpoint. Three timeouts later, the switch indicates that the endpoint does not have a supplicant. It then attempts to use MAB to authenticate it. This step is usually done by the switch and does not involve the RADIUS.
2. RADIUS MAC Authentication
The switch initiates MAB first by accepting a single packet from an interface to identify where the endpoint’s MAC address originates from. Once the source MAC address is identified, the packet is discarded and the switch creates a RADIUS access-request-message with the MAC address of the machine/user as the identity. The RADIUS server then receives the access-request message and performs MAC authentication.
3. Authorization
In this step, the RADIUS authentication server will make the decision if the user/device has to be given access as well as the level of access the client is to be provided with. The RADIUS server transmits the access-accept after which the user/machine can access the network. RADIUS may use authorization options like Downloadable ACLs (dACLs), Dynamic VLANs (dVLANs), and Security Group Tags (SGT).
MAC Auth Bypass Modes
As a default setting, MAB supports one device per switch port and a violation is flagged if more than one MAC address source is detected. This can, however, be changed. The following modes can be set up in MAB. The modes can be set up at the switch and do not involve any RADIUS setting.
Single-Host Mode
Single-Host mode is the default of MAB. If more than one MAC address is detected, it raises a security violation.
Multi-Domain Authentication Host Mode
Multi-Domain Authentication Host Mode allows two source MAC addresses to be authenticated, one through the voice VLAN and the other through the data VLAN. This is useful when a VOIP phone and a PC are connected through the same switch port. In this mode, a violation will be flagged if more than 2 MAC addresses are identified.
Multi-Authentication Host Mode
This mode is used in a situation where the switch port is linked to another switch and multiple source MAC addresses need to be authenticated.
Multi-Host Mode
This mode allows access to multiple source MAC addresses by authenticating the first source MAC address. The other source MAC addresses are automatically permitted access after the authentication of the first source.
MAC Address Filtering
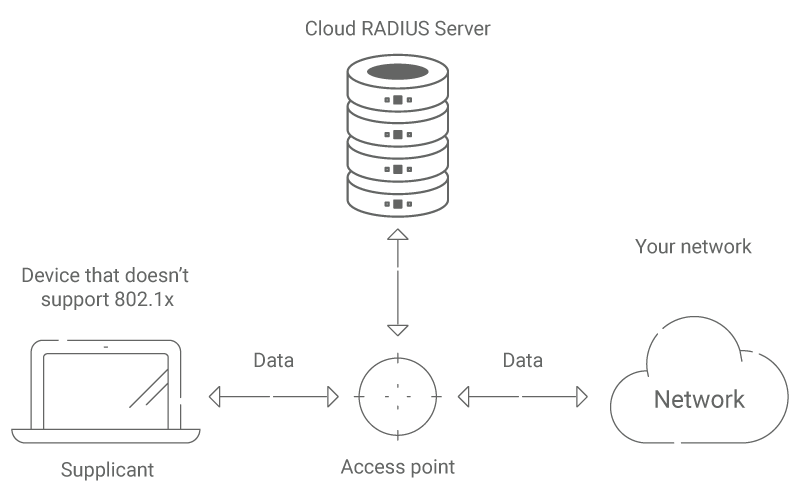
MAC address filtering is a security protocol that allows you to list the MAC addresses of devices that you want to access the network as well as the list of devices that are denied access. It’s an access control protocol that helps you control who has access to your network. When RADIUS MAC Auth is enabled, the RADIUS will verify if a device requesting access is on the allowed access list and will provide access only if the device’s MAC address is listed as approved.
Though not considered the safest protocol for network security, MAC address filtering can help with devices that do not support 802.1X and are being authenticated using RADIUS MAC authentication.
Here is how MAC address filtering works with RADIUS MAC Authentication.
- Create a list of MAC addresses for the devices that are allowed access to the network.
- The list can also include the ports to which a particular MAC address gets access.
- RADIUS will check the allowed access list when a device requests access to the network. If the MAC address is listed, RADIUS will allow access to the port the device has been listed to provide access.
The process of setting up MAC address filtering is considered complicated and not very efficient for network security. However, when using RADIUS MAC auth to authenticate devices that don’t support 802.1X, MAC address filtering can be beneficial as you can limit access to only the devices that you want to connect to your network. MAC Auth Bypass when used with MAC Address Filtering works like an additional layer of security check these devices have to pass before getting access.
Get Better Network Visibility of Devices that don’t support 802.1X
Most industries today use at least some devices that do not support 802.1X like smart robots in manufacturing, smart kitchen appliances in hotels and restaurants, or Medical IoT devices to monitor heart rate or blood sugar levels to name a few. These devices leave a company vulnerable to cyber attacks as they do not fall under regular network security measures and are often easy gateways for hackers to infiltrate a network. But because of the utility they provide, it’s simply not an option to omit them from our networks entirely.
MAC auth bypass when used with MAC address Filtering can help bring these otherwise unmanaged devices under the purview of network security by first making them traceable and then limiting their access to their needed level in the network with the help of dynamic access.
SecureW2’s Cloud RADIUS supports MAB and MAC address filtering, segmenting devices with dynamic access lists and VLAN assignments in a similar manner to 802.1X. If you use devices that do not support 802.1X authentication protocol, manage and account for them with MAC auth bypass and MAC address Filtering to extend your network visibility to these unmanaged devices. Book a free Demo to know how we can help you reduce these risks and make your IoT devices more secure.



