Need a solution for your network authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) requirements? RADIUS has been around for decades, used by thousands of organizations. Without a RADIUS server, authentication would have to occur at the access point (this would require some pretty powerful APs), such as in the case of PSK (pre-shared key) authentication. PSK authentication only requires a single password to be remembered, so it is simple to implement.
But is PSK secure enough? An attacker can easily read a device’s wireless settings and view the pre-shared key in plain text. It is no secret that a PSK network is vulnerable to various attacks,74% of Data Breaches start with privileged credential abuse.
A RADIUS network eliminates this risk of leak of the private information of your organization to snooping outsiders by enabling individual users to authenticate with unique credentials.
If you’re using Windows 2022/2019/2016, you already have RADIUS capability. Before using the third-party servers, look into the Network Policy Server (NPS) as a RADIUS solution.
NPS as a RADIUS Server
In Windows, RADIUS servers are implemented through Network Policy Server (NPS). NPS allows the creation of both access policies for connection requests and configures Network Access Servers (NAS) to forward connection requests to remote RADIUS servers, which helps load-balancing the connection requests.
NPS performs AAA services for the connection requests from:
- Wireless network
- Virtual Private Network (VPN) remote access
- 802.1x switches
- Dial-up
- Router to router connections
NPS is designed for on-premise infrastructure, so it may not be a suitable choice for organizations looking for cloud solutions. Also, it doesn’t blend well in a non-Windows environment. With the rise in cloud computing, compatibility with the cloud is a must for any technology seeking longevity in this industry.
Pre-requisites for Configuring a Microsoft RADIUS Server
Before you configure RADIUS, please check for the below requirements:
- Windows 2022 Installation
- Here are step-by-step instructions.
- Windows 2022 Desktop Experience
- Devices that support WPA2-Enterprise
- An activated Domain Controller for Windows
- Active Directory installed on your Windows
- Here are step-by-step instructions.
- NPS Installation
- Follow the instructions in the guide
How to set up a Microsoft RADIUS Server
Step 1 – Create a New Group on AD
To facilitate the users with permission to access your network, create a group in the Active Directory Domain. Add all of the users that will authenticate through your new RADIUS.
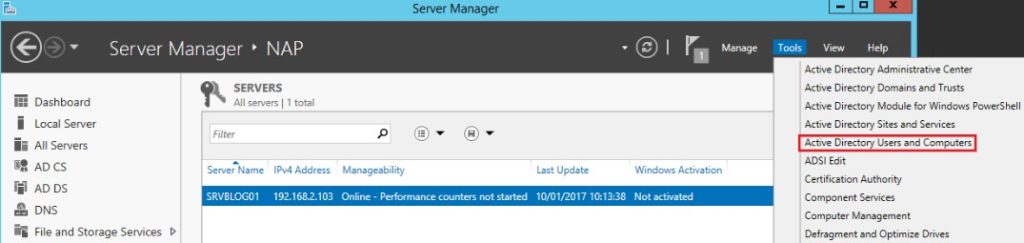
- Click on “Active Directory Users and Computers” under Tools in Server Manager:
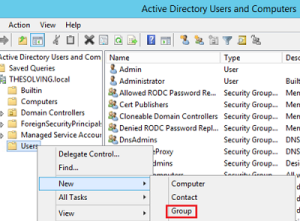
- Now to create a new group, right click on “Users”, followed by “New” to choose “Group”:
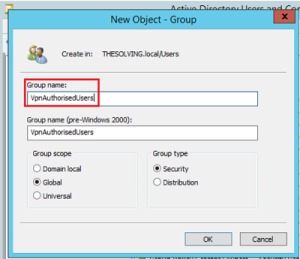
- Name the AD group under “Group name”:
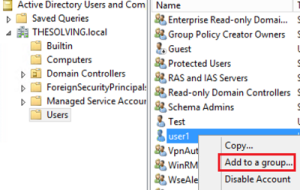
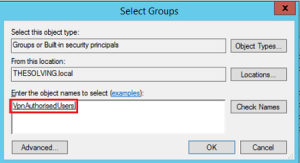
- Right click on the the user (here user1) you want to authenticate throught the new group (here VpnAuthorisedUsers):
- Now select the newly created group (VpnAuthorisedUsers):
Step 2 – Add Network Policy and Access Services Role
- Add Roles and Features in the Server Manager console:
- Select the type to install roles and features:
- Select the server where you want the role to be installed:
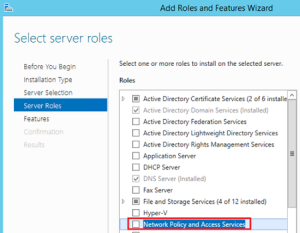
- Now add Network Policy and Access Services:
- Then add the features you need in the wizard.
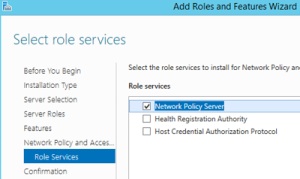
- Add role services, select “Network Policy Server”:
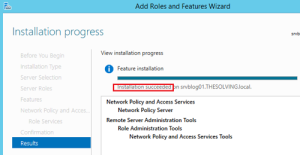
- Confirm and finish the installation:
Step 3 – Configure RADIUS using NPS
Follow the pictorial instructions and you will have RADIUS configured.
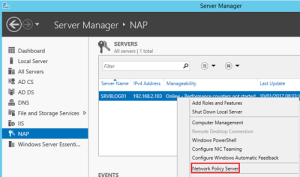
- Select “Network Policy Server” for the server you installed the role (server is added under NAP):
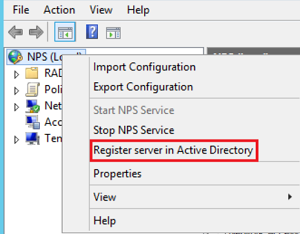
- Snap-In NPS to AD:
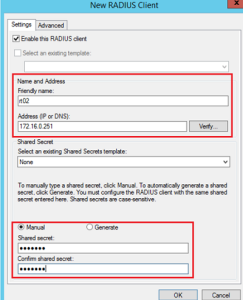
- Create a new Radius Client under the option “RADIUS Clients and Servers”.
- Give a name and IP for the device that will forward the authentication request to the RADIUS. Also, a password(shared secret) for the network:
- Radius is now configured.
Microsoft RADIUS Security Concerns
Shared secrets are a weak form of authentication security. The server generates a keypair and is copied to every client machine. When connecting to the server, the client will check that the public key presented matches the one they have cached for that server.
An attacker can easily harvest the server’s private key and can act as an authenticated server. The client believes it is talking to an authentic server and there is nothing that can be done to prevent this because pre-shared secrets have no revocation mechanism.
Digital certificates offer the best security. Certificates are similarly easy to authorize. Part of the authentication process involves the RADIUS server checking a Certificate Revocation List (CRL) to ensure the certificate is not revoked or expired. If an admin realizes that a certificate has been compromised, they add it to the CRLand all clients will immediately know because the online revocation checks will fail. The revocation mechanism is very important and is one of the major advantages of certificates.
SecureW2 allows you to easily generate a custom private CA and export the .p12 to then import into NPS. Or, you can import your AD CS certificates and use SecureW2 to enroll end-user devices to self-service themselves for client certificates for your AD CS Certificate Authority.
Your Windows Server RADIUS is now ready to go! Users will need to be manually added and removed from the security group unless you use an onboarding solution like the one offered by SecureW2. Click here to check out our world-class automatic enrollment suite JoinNow.
Cloud RADIUS: A Great Replacement for Microsoft RADIUS Server
NPS may be a good option for the Windows environment but there are major shortcomings you must consider before you decide.
NPS is an on-premise server. On-prem infrastructures have various vulnerabilities ranging from intruders to calamities. One of the most frequent and severe threats is a zero-day attack, Mandiant Threat Intelligence observed roughly 80% of successful cybersecurity breaches stem from zero-day attacks.
Cloud Radius networks are typically much better protected and highly resilient compared to their on-premise counterparts. End users and IT admins alike value both the convenience and versatility of cloud computing services and its quickly overtaking on-site servers.
There is no native ability to connect NPS with cloud directories. It doesn’t even work with Microsoft’s own cloud platform, Azure AD (Microsoft Entra ID), without workarounds and proxy servers. This means that NPS may not be a suitable choice for organizations looking for cloud-based solutions.
Cloud RADIUS is a turnkey solution that allows you to bridge the gap between on-prem and cloud without expensive forklift upgrades. SecureW2’s RADIUS and Managed PKI Services integrate seamlessly with every major vendor. We’ve worked with countless organizations to migrate to an all-cloud environment using Azure with Cloud RADIUS.
Check out our pricing page to see how we can help you.