Key Points
- Group Policy manages on-prem devices, while Intune delivers cloud-based, over-the-air policy enforcement for remote and hybrid environments.
- Intune integrates compliance policies with Conditional Access, ensuring only secure, compliant devices access organizational resources.
- SecureW2 simplifies migration from AD to Intune with Managed PKI, Cloud RADIUS, and certificate-based authentication for passwordless security.
Microsoft has many policy management tools to secure client devices in an organizational environment. Microsoft Group Policy and Intune Profiles are commonly used solutions in different environments, catering to different devices. While Group Policy works for devices in a Windows domain in an on-premise Active Directory domain, Intune is a cloud-based mobile device management solution that lets administrators apply policies over the air for remote devices.
As remote work becomes more permanent, the traditional policy enforcement approach through on-premise domains is losing relevance. In this context, Intune offers a cloud-based alternative for policy enforcement and compliance maintenance in a hybrid environment.
This article is a comprehensive and up-to-date comparison between Group Policy and Intune Profiles. By the end, you will be equipped with the knowledge to make an informed decision. Whether you choose an on-premise or cloud setup, you can proceed with confidence in your choice to secure your devices.
What Is Microsoft Group Policy?
Microsoft Group Policy is known to be the default standard for user and device policy settings in a Windows environment. The Group Policy Object helps administrators apply settings, monitor end users, and configure functional policies. The Group Policy Object is populated with end users and device configurations to obtain standardization without manual interventions.
Microsoft GPO allows administrators to enforce granular policies, i.e., policies for a specified group, user, or device, to ensure that the administrator can see who and what is accessing the network. This also manages specific roles and policies for specific users and devices for better network management. However, group policy settings are applied to users and devices in an on-premise Active Directory domain on the same network. The group policy settings will fail to apply or refresh if the user or device is outside the Active Directory domain controller network.
In the past, devices that needed direct connectivity with the on-premise AD domain could use a VPN to create a secure tunnel to the organizational network through any wi-fi network. The connection between the client and the network was safe but vulnerable to malware and ransomware attacks, as a VPN could increase the chance of the device being infected with malicious software.
What is Microsoft Intune?
Microsoft Endpoint Manager, or Intune, is a cloud-based mobile device management solution that manages iOS and Android mobile and Windows, Ubuntu, and Android Open Source Project (AOSP) client devices. Intune allows administrators to manage all users and devices from a single console, ensuring device compliance and network security. The console can also occasionally distribute or remove work-based applications.
When deployed with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint or a third-party service, Intune provides thorough endpoint security that automatically manages and remedies threats. Microsoft Intune lets the admin monitor the network through device health through the comprehensive reports provided by Intune on compliance, usage, and security risks as and when detected.
You can also add third-party tokens and digital certificate solutions for users to auto-enroll themselves for policies and applications and deploy them to their devices.
Microsoft GPO vs Microsoft Intune- Comparison
Microsoft GPO and Intune are similar in providing policy management for devices and users in an organization. Policies decide access rules for users and devices since they determine who gets to access what in an organization. While the Group Policy is an Active directory feature, Intune is cloud-based and helps secure users and devices in an organization. Here are some differences between Microsoft GPO and Intune:
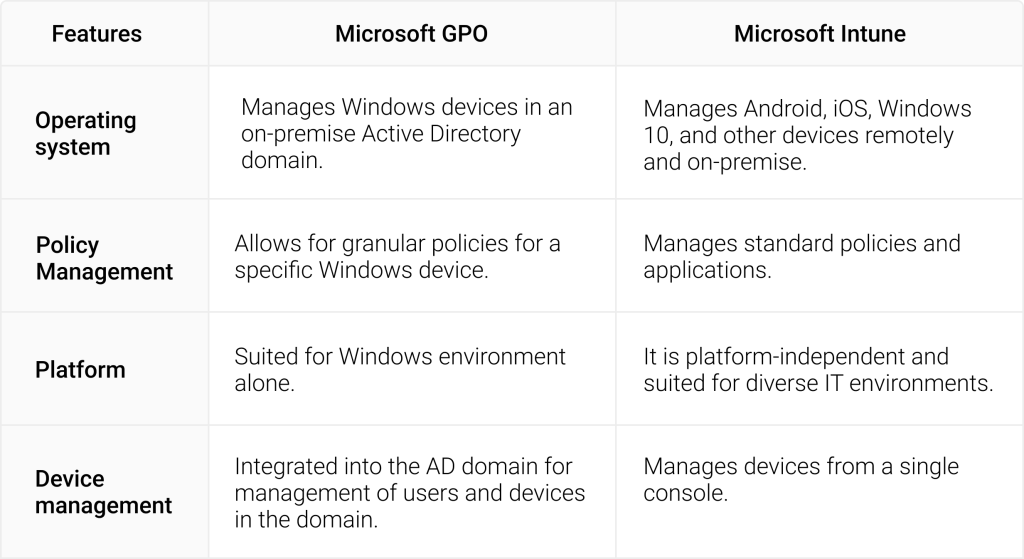
If an organization is looking to move from Group policy to Intune, there are some solid use cases for both, as they have pros and cons. Intune is the way to go if you are looking at a cloud-based setup for your users and devices. However, using a mix of GPO and Intune to manage both on-premise and cloud devices for enhanced security would be prudent.
How to Enrol Devices to Intune Using Group Policy
If you are a Microsoft user, you can automatically enroll your hybrid Azure AD-joined Windows devices in Intune. You can use the Intune enrollment GPO for hybrid Azure AD-joined devices, as they already have Azure AD registered devices.
Prerequisites for Intune Enrollment With Group Policy
- A valid Intune license.
- Activation of auto-enrollment for client devices.
- Windows devices with Windows 10 and later.
- Hybrid Azure AD joined devices.
Configuring Intune Group Policies for Auto-Enrollment
Once the above prerequisites are met, you can auto-enroll your devices to Intune. The prerequisites are very important when enrolling your devices in Intune MDM. To begin enrolling, you have to follow these steps:
- Click on Group Policy Management (gpmc.msc) on the Start menu of your domain controller or server.
- Right-click on the Group Policy object and click New.
- Provide the GPO name to deploy client devices for enrollment.
Image Courtesy: https://www.anoopcnair.com/windows-10-intune-enrollment-using-group-policy/
Windows 10 Intune Enrollment using Group Policy | Automatic Enrollment | AVD
- Edit the MDM policy by right-clicking on the MDM name.
Windows 10 Intune Enrollment using Group Policy | Automatic Enrollment | AVD
- Click on the policy Nodes.
- Now, click on the MDM folder. Select Enable Automatic MDM Enrollment Using Default Azure AD credentials. This policy ensures the device in Azure AD is configured for the MDM.
- Click Enable to allow hybrid Azure ad joined devices to enroll in Intune.
- You will now pick Credential Type and choose credentials as the default option.
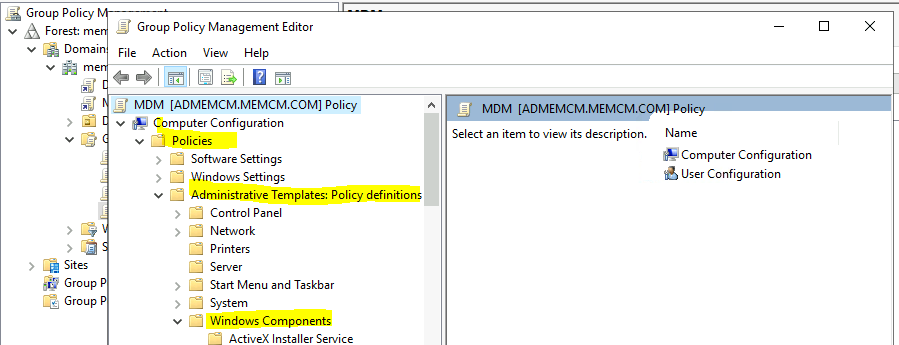
- Click OK for Policy creation.
Windows 10 Intune Enrollment using Group Policy | Automatic Enrollment | AVD
Assigning Intune GP to Organization
Now, link the group policy to the Organizational Unit of the Active Directory.
- Launch a prompt command to type DSA.MSC.
- Right-click Domain and select New – Organizational Unit.
- Enter the Name of the OU = WVD.
- Click OK to complete the OU creation process.
Windows 10 Intune Enrollment using Group Policy | Automatic Enrollment | WVD
- Navigate back to the Group Policy Management console.
- The new OU would be visible there.
Windows 10 Intune Enrollment using Group Policy | Automatic Enrollment | AVD
- Right-click on the new OU in the Group Policy management console.
- Link and existing GPO.
- Select the MDM group policy from the list.
- Click OK to complete the GPO assignment.
Windows 10 Intune Enrollment using Group Policy | Automatic Enrollment | WVD
Once the Windows 10 MDM/Intune enrollment group policy is applied to the device, you can see the Intune policy details on the accounts page from the settings page.
Microsoft’s Group Policy Analytics tool allows you to migrate from on-premise to the cloud. This tool analyzes and imports the required settings and shows what can be imported and set up with the Intune MDM solution.
Device Compliance Policy In Intune
Microsoft Compliance policies in Intune are rules that examine and configure your managed devices to secure organizational data and applications for a secure network environment. Any managed device should comply with all the conditions set by the administrator of the Intune policy manager. If you have devices that do not meet the configuration requirements, a device can be isolated and quarantined from the organizational network.
MEM Intune provides easy migration from GPO and integrates the compliance results with Microsoft Entra Conditional Access for extra security. Conditional Access enforces access control by ensuring only compliant devices can access organizational resources, data, and applications.
Leverage SecureW2’s PKI to Migrate From AD to Intune Easily
This article provided an overview of the benefits of group policy and Intune profiles and how they would fit into an organization’s network structure. Where larger organizations with stricter compliance need to benefit from legacy AD, organizations like educational institutions with a mix of managed and BYOD devices can benefit from a cloud-based mobile device management solution like Intune.
The shift from AD to Intune seems complicated, but Securew2’s Managed Gateway APIs let you shift to a cloud-based certificate-enabled solution to secure your network. You can use your existing Azure AD credentials to enroll devices for certificate-based authentication.
SecureW2s Cloud RADIUS lets you implement diverse policies through its policy engine so that your access rules are taken care of, and the auto-revocation of certificates (exclusive to Intune) helps you revoke unused certificates on time to avoid any unauthorized access.
Click here to learn more about our passwordless solutions now.