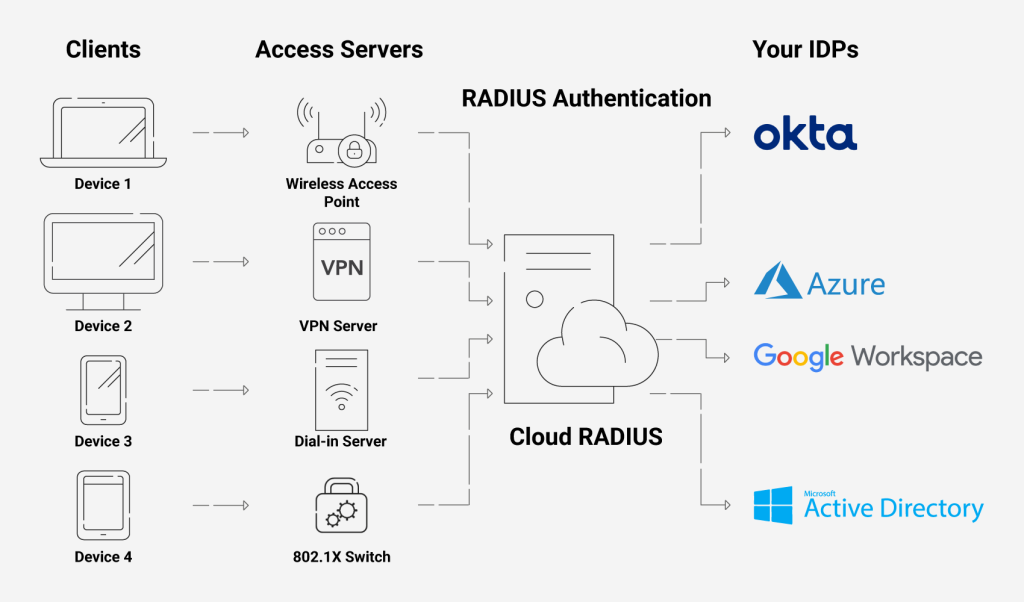
The name RADIUS needs no introduction whenever you imagine a wired or wireless authentication server. Commonly referred to as AAA servers, RADIUS performs the core task of Authentication, Accounting, and Authorization within an 802.1x infrastructure. As the de facto incumbent, Microsoft has evolved its RADIUS server over time to meet the authentication needs of its customers.
When we talk about the evolution of the Windows Server, the 2008 edition holds a significant place in history. Although rarely used now, we felt it still might be a good time to assist the existing customers of Windows 2008 servers in configuring the same. But as you might know, most of these servers are on-premise in nature and catch a great deal of attention from hackers.
Here’s a recent incident of an update causing authentication to fail, affecting primarily the on-premise setups. But we are not here to judge on-premise servers; we leave that for you to decide. Let’s get back to configuring the evergreen Windows 2008 server.
Before configuring the Windows Server 2008, ensure that you met the following requirements for successfully configuring the Windows 2008 server.
Prerequisites for Windows RADIUS Server 2008:
❖ System Requirements:
- Processor: You need a processor of at least 1.4 GHz clock frequency for x64 processors. But Microsoft recommends using 2GHz for smooth functioning.
- RAM: The minimum requirement of RAM is 512 MB. But Microsoft recommends using the RAM of 2GB capacity.
- For 32-bit systems,
- 4 GB is recommended for Windows Server 2008 Standard.
- 64 GB is recommended for Windows Server 2008 Enterprise and Windows Server 2008 Datacenter.
- For 64-bit systems,
- 32 GB is recommended for Windows Server 2008 Standard.
- 1 TB is recommended for Windows Server 2008 Enterprise and Windows Server 2008 Datacenter.
- 2 TB is recommended for Windows Server 2008 for Itanium-Based Systems.
- Disk space: You need a minimum disk space of 10 GB or more, but Microsoft usually recommends using 40 GB or more disk space. Also, the disk space requirements vary with the processor and RAM used in the system.
- For 32-bit systems,
❖ Active Directory Setup:
You must update the Active Directory environment before adding the domain controller.
❖ Application Compatability:
You can check the compatibility of your network by using the Microsoft Application Compatibility Toolkit (ACT), now known as Windows Analytics.
❖ Server Core Installation:
While installing this, you need to install one of the following options:
- Windows Server 2008 VERSION (Full Installation): Select this option for the complete installation of Windows Server 2008.
- Windows Server 2008 VERSION (Server Core Installation): Select this option for a minimal server installation of Windows Server 2008.
Overview of Windows RADIUS Server 2008 Configuration:
- Install and set up Windows Server 2008/Windows Server 2008 R2.
- Install Active Directory Domain Services (ADDS) to configure the new domain.
- Install Certificate Authorities (CA) with Active Directory Certificate Services (ADCS).
- Install NPS ( Network Policy Server).
- Configure Certificate Authorities (CA), i.e., Active Directory Certificate Services (ADCS) for Certificates.
- Configure NPS ( Network Policy Server) for the authentication protocol.
- Configure RADIUS.
- Define Network policies for users/devices.
- Configure Access Point.
- Set up zero clients, and select 802.1x authentication.
- Configure Wireless Connection Request.
Configure Windows 2008 RADIUS Server:
Now we will see each step involved in configuring Windows 2008 server in detail:
Install and Configure AD DS:
For configuring ADDS, follow the given instructions:
- Navigate to Windows Server 2008.
- Click Start.
- Click Server Manager.
- Navigate to Role Summary.
- Click Add Roles.
- Navigate to the Before You Begin page and click Next.
- Navigate to the Select Server Roles page.
- Select the Active Directory Domain Services.
- Click Next.
- Click Install on the Confirm Installation Selections
- Navigate to the Installation Results page and click Close.
- ADDS is installed.
Now for the configuration of the new domain, continue the following steps:
- Navigate to Welcome to the Active Directory Domain Services Installation Wizard page, and click Next.
- Navigate to Choose a Deployment Configuration page and click Existing forest.
- Click Add a domain controller to an existing domain, then click Next.
- Click Next on the Additional Domain Controller Options.
- Select DNS server.
- Click Next and click Yes to continue.
- Click Next on the Location for Database, Log Files, and SYSVOL page, and choose the required folder locations.
- Click Next on the Directory Services Restore Mode Administrator Password
- Review your selections on the Summary.
- Click Finish on Completing the Active Directory Domain Services Installation Wizard.
- Click on the Reboot on completion button to automatically restart the server.
Install AD CS and NPS :
- Navigate to Server Manager.
- Select Roles and Click Add Roles.
- Click Next on the Before you Begin.
- Select Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) and Network Policy and Access Services.
- Click Next.
- Click Next on Network Policy and Access Services.
- Navigate to Role Services and select Network Policy Server.
- Click Next.
- Select Create a self-signed certificate for SSL encryption and click Next.
- Click Next on the Introduction to Active Directory Certificate Services.
- Select Certification Authority on the Select Role Services page and click Next.
- Select Enterprise on Specify Setup Page and Click Next.
- Select Root CA on Specify CA Type Page and Click Next.
- Select Create a new private key on the Set Up Private Key Page and Click Next.
- Click Next on Configure Cryptography for CA.
- Enter details on Configure CA Name page and click Next.
- Enter the validity period on the Set Validity Period page and click Next.
- Click Next on Configure Certificate Database.
- Click Next on the Web Server (IIS).
- Click Next on the Select Role Services.
- Click Install on the Confirm Installation Selection.
- Click Close.
Now the AD CS (Active Directory Certificate Services), Web Server (IIS), and NPS are installed successfully.
Configure Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) for Certificates
Start MMC on the server and open the Console page.
- Select Certificates on Add or Remove Snap-ins.
- Click ADD and click OK.
- Select Computer Account on the Certificates snap-in page and click Next.
- Select Local Computer on the Select Computer page and click Finish.
- Click OK on Add or Remove Snap-ins.
- Navigate to Console Root and expand the Certificates tab.
- Select Personal and click Certificates.
- Select All Task and Request New Certificates.
- Click Next on the Certificate Enrollment.
- Select your Domain Controller and click Enroll.
- Click Finish.
Now we have successfully configured certificates in the Windows server.
Configure NPS ( Network Policy Server) and RADIUS authentication.
- Click on the Start button and select Administrative tools.
- Click NPS on the Network Policy Server.
- Select Register Server in Active Directory and click OK.
- Click OK.
- On the NPS (Local) page, select RADIUS server for 802.1x Wireless or Wired Connections.
- Click Configure 802.1x.
- Select Secure Wireless connections on the Configure 802.1x.
- Type Name and click Next.
- Add RADIUS clients on the Configure 802.1x page and click Next.
- Type the following details on the New RADIUS Client page.
- Name
- IP Address
- Shared Secret (Manual)
- Click OK and click Next.
- Select Microsoft Protected EAP (PEAP) on the Configure 802.1x page.
- Click Configure.
- Select Secured password on the Edit Protected EAP Properties page and click Edit.
- Enter the Number of authentication retries and click OK, and click Next.
- Select Groups and click Next.
- Click Next again and click Finish.
- Restart NPS again.
Define Network Policies for users/devices.
You can follow the given steps for Defining the network policies.
- Navigate to the NPS console and click NPS (local).
- Click and expand Policies.
- Select Network Policies.
- Click New.
You can use the Network Policy Wizard to create and add new conditions, constraints, and setting to the network policies.
Administrators can define and implement a wide range of policies using our Cloud RADIUS during lookup policies. For instance, depending on the time of day, you can decide whether to accept or reject people and devices. You may also restrict access to devices running a specific operating system.
You can also select the already created WiFiAP by following the given steps:
- In the left navigation bar, select Network Policies.
- Select the existing WiFiAP and click Properties.
- Select the Constraints on the WiFiAP Properties page.
- Select the desired Authentication Methods and click OK.
- Select the Settings on the WiFiAP Properties page.
- Click on Encryption and select the Strongest Encryption.
- Click OK.
Set up Zero Clients, and Select 802.1x Authentication
- Navigate to the Control panel and open the Network and Sharing center.
- Click Change adapter settings.
- Select Local Area Connection and click Properties.
- Select Authentication and click Enable IEEE 802.1x authentication.
- Select the desired protocol in the dropdown button.
 Configure Wireless Connection Request
Configure Wireless Connection Request
- Navigate to the Control panel and open the Network and Sharing center.
- Click Manage Wireless Networks.
- Select Manually Create a network profile.
- Enter your SSID in Network Name and click Next.
- Click Change Connection settings.
- Select Security and click Settings.
- Select the Trusted Root CA and click OK.
- Navigate to Advanced Settings.
- Select Specify Authentication Mode and click OK.
Drawbacks of Windows RADIUS Server
Traditional on-premises RADIUS servers are prone to several security flaws and vulnerabilities. On-premise infrastructure commonly uses Windows RADIUS servers, built from NPS, which have many susceptibilities of their own that hackers frequently exploit in zero-day attacks. On top of that, they need a great deal of time and expertise to set up.
Also, because of its physical accessibility, the NPS server’s on-premise presence makes it vulnerable to various physical security threats, from intruders to disasters – or just power outages. Given the costs of maintaining highly-secure physical locations, there’s rarely a circumstance in which on-prem works out to be cheaper than cloud RADIUS.
Somewhat counterintuitively, cloud networks are typically much better protected and highly resilient compared to their on-premise counterparts, mainly due to economies of scale.
NPS, built for on-prem AD environments, has significant drawbacks when integrating with other Microsoft-owned cloud-based products, such as Azure AD. If you wish to use Azure with NPS, you’ll need to use a different authentication server or proxy to make the procedure easier. These procedures are not only time-consuming and challenging, but they are also very costly in nature.
Cloud RADIUS: The Present and the Future
Windows Server 2008 edition has been a bedrock for network admins over the years and has witnessed almost the entire Microsoft ecosystem evolve over time. But it is hard to ignore its drawbacks, which have become more of a security liability than a strength in the modern day. Windows 2008 server has struggled to keep up with the advancements of the cloud, so consider that it might be time to retire the 15-year-old server and upgrade for the sake of your network security.
Migration to the cloud has immense advantages over being in an on-premise world full of security threats, and what’s better than using our innovative Cloud RADIUS! You can eliminate almost all of these drawbacks by using a cloud-based server like Cloud RADIUS backed by SecureW2.
Our Cloud RADIUS, powered by advanced Policy Engines, gives you the power to deny/allow users access based on many attributes, such as user/device attributes or even time of day. Also, our Cloud RADIUS is designed for vendor neutrality so that you can use it with any IDP. Using its servers, you can also enforce policies with real-time user lookup against Azure, Okta, & Google Workspace.
Besides not needing lengthy setups, Cloud RADIUS is resistant to on-site risks like outages and burglars. It doesn’t need to be installed at each location of your company because it is hosted in the cloud and has built-in redundancy.
If you are interested in taking that first step toward security for your organization, look no further and click here to inquire about pricing.



 Configure Wireless Connection Request
Configure Wireless Connection Request