Active Directory (AD) and Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) are two terms frequently used regarding directory services. These solutions are essential frameworks for managing user identities, resources, and network configurations in an IT infrastructure.
While LDAP is a standardized protocol for accessing and preserving directory information, Microsoft’s Active Directory is an extensive service, providing extra functions for Windows-based systems. LDAP and Active Directory work together. In this article, we’ll explain their differences and how they work alongside one another.
What is LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol)?
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol, or LDAP is a protocol standards-based specification for interacting with directory data. LDAP is designed to provide extremely fast read/query performance for a large dataset.
Imagine a website with a million registered users with thousands of page requests per second. Without LDAP, whenever users click a page, even for static page viewing, you will probably need to interact with your database to validate the user ID and digital signature for this login session. LDAP lets you easily offload the user validation and gain significant performance improvement.
LDAP is not just for user validation, any of the following properties provide an opportunity to use LDAP:
⦁ Locating ONE piece of data many times
⦁ Disregarding logic and relations between different data
⦁ You don’t often update, add, or delete the data
⦁ The size of each data entry is small
⦁ Communicating with a directory
⦁ Having small pieces of data in a centralized location
For a more in-depth look, check out the page all about LDAP.
How Does LDAP Authentication Work?
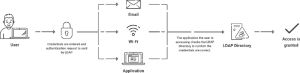
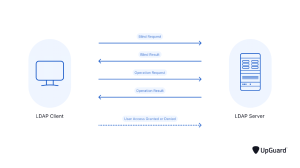
LDAP authentication is based on a binding operation. When the user and the directory server connect through the LDAP Bind operation, an LDAP-enabled application transmits the user’s credentials to a directory service such as Active Directory for validation.
⦁ The user inputs their credentials.
⦁ The LDAP server receives credentials using the LDAP protocol.
⦁ The LDAP server determines the credentials’ validity by comparing them to the database and then generates the response.
⦁ The LDAP protocol receives the response from the LDAP server and returns it to the application.
⦁ When an application receives an answer, it takes appropriate action. For example, it may log the user in if the response is yes or output “Username or password incorrect” if the response is no.
Risks of the LDAP Authentication Protocol
Since LDAP facilitates connections to private network resources, cybersecurity concerns are connected. hackers have found flaws in LDAP authentication throughout time. The most dangerous of these vulnerabilities is LDAP injection.
An LDAP injection is a type of cyberattack where malicious code is injected into a web application to get access to confidential data held in LDAP directories. The implanted code uses LDAP metacharacters to change legitimate requests from LDAP clients to achieve malicious objectives. An account takeover, user privilege escalation, or data breach might result from an LDAP injection. Cyberattackers can easily interact with LDAP and cause LDAP injections when the authentication server fails to validate the authenticity of LDAP client queries.
What is Active Directory?
To understand the correlation between LDAP and AD, we must first understand exactly what an Active Directory is. It’s a Directory Service, a software system that stores, organizes, and grants access to information in a computer operating system’s directory. In software engineering, a directory is a map between names and values. It allows the lookup of named values, similar to a dictionary.
How Does Active Directory Work?
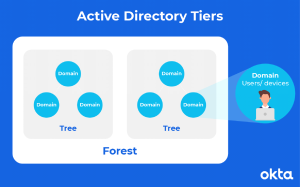
Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS), a Windows Server operating system component, is the primary Active Directory service. Domain controllers (DCs) are servers that operate AD DS. Typically, an organization will have numerous DCs, one copy of each DC for the whole domain. To keep everyone up to speed, changes made to one domain controller’s directory, such as changing a password or deleting user accounts, are replicated to the other DCs.
A Global Catalogue server is a DC that keeps a partial copy of all items from all other domains in the forest and a complete copy of all objects in its domain directory. This allows users and applications to locate things in any domain within their forest. Desktops, laptops, and other Windows-based devices can be part of an Active Directory system but can not run AD DS. AD DS depends on well-established protocols and standards, such as DNS (Domain Name System), Kerberos, and LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol).
It’s critical to know that Active Directory is exclusive to Microsoft installations hosted on-premises. Azure Active Directory is used in Microsoft Cloud settings and fulfills the same functions as its on-premises counterpart. Although Azure AD and AD are distinct, they could collaborate if your company uses both cloud-based and on-premises IT infrastructures (a hybrid implementation).
How Does LDAP Work With Active Directory?
Think of LDAP as the language that AD can speak. The task of LDAP is to extract information stored in AD. When a user looks something up in AD, like a computer or printer, LDAP is used to find the relevant information and present the results to the user.
Active Directory LDAP Server Advantages and Disadvantages
Both LDAP and Active Directory have advantages and disadvantages. Organizations may better comprehend LDAP vs. AD by weighing the pros and cons of each of them.
Advantages
The following are the key advantages of LDAP use:
⦁ It has broad acceptance in several industries.
⦁ It is an approved, standardized web protocol.
⦁ Its architecture is very adaptable, and it is offered as open-source software.
⦁ It is very scalable, quick, and lightweight.
Active Directory also provides several advantages, such as:
⦁ Its great degree of customization makes it simple to use, administer, and control access.
⦁ Compared to other directory services, it offers more security because of complex group policies and trust layers.
⦁ Features for compliance management, including audits and data encryption, are included.
⦁ Several versions are available to meet different requirements, such as cloud security and federation services.
Disadvantages
LDAP is a legacy technology with several drawbacks. These are obstacles that organizations may find challenging to overcome:
⦁ Its age: Early on in the history of the internet, LDAP was established.
⦁ It is not appropriate for web-based and cloud applications.
⦁ Maintenance and setup are typically difficult and need a specialist.
Active Directory also has several disadvantages. The following are some drawbacks to consider:
⦁ It is limited to Windows operating systems.
⦁ Since Active Directory oversees the network, its failure will destroy the entire system.
⦁ The expense of setup and maintenance might be substantial.
⦁ Because it needs on-premises infrastructure, legacy AD is restrictive.
How Does Active Directory Use the LDAP Protocol?
Microsoft Active Directory is an application that maintains a centralized, hierarchical database with data on people and devices. AD offers a strong identification and access control system. Using a single set of login credentials, AD is used by businesses to authenticate users for access to on-premises resources.
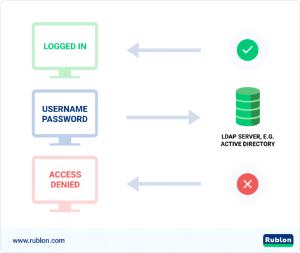
Applications often query and connect with directory services using the LDAP protocol. But LDAP can also handle authentication data when used with Active Directory. By binding to the directory service database, it does this. When users bind, the LDAP server verifies their identity and authorizes them to access resources according to their rights.
AD allows organizations to deploy LDAP instead of Microsoft’s default authentication technique, which employs the more complex Kerberos protocol. LDAP offers a quick and simple authentication mechanism. It compares the user’s login credentials to the data kept in the AD database. LDAP gives the user access if they match.
The Differences Between Active Directory and LDAP
AD is the most widely used directory server and uses LDAP to communicate. LDAP is the core protocol used to query, maintain, and determine access for AD to function. It’s also often used for user authentication.
Though many use LDAP and AD interchangeably, they are two different things. Consider LDAP as the language that AD can speak, so AD servers are sometimes called LDAP servers. The task of LDAP is to extract information stored in AD. When a user looks at something up in AD, like a computer or printer, LDAP is used to find the relevant information and present the LDAP query to the user.
Another difference between LDAP and AD is how they handle device and user management. Active Directory has a function called Group Policy (GPO) which allows admins to control Windows devices and offers Single Sign-On abilities, neither of which is available with LDAP. Regarding ability, there’s much to be desired with LDAP, meaning AD-domain admins are on their own when implementing LDAP-compatible devices and servers.
LDAP vs Active Directory: Navigating Identity and Access Management
Many organizations struggle with the decision to move past using LDAP, as it’s often tied to their long-standing Active Directory structure. Therefore, active Directory and LDAP have been integral parts of organization infrastructure for years. However, using them exposes organizations to vulnerabilities as hackers develop more sophisticated attacks such as LDAP injection attacks.
As organizations shift to cloud-based identity management solutions and directory services, addressing these risks and considering alternatives is critical. SecureW2’s Managed Cloud PKI provides a solid foundation for cloud-based Identity Providers such as Azure AD/Entra ID. Besides addressing conventional issues, our solution provides a secure bridge for organizations switching from Active Directory to Cloud architecture.
Contact us today to learn how SecureW2’s Managed Cloud PKI can improve your identity and access management.