Extensible Authentication Protocol-Transport Layer Security (EAP-TLS ) and Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol (PEAP ) are both authentication protocols used in the 802.1x framework, but they are not the same. The key difference between them is their authentication procedures. EAP-TLS requires mutual certificate-based authentication, while PEAP only requires server-side certificates and uses user-credentials for client-side authentication. Learn more about EAP-TLS authentication and how it works.
A High-Level Comparison: EAP-TLS vs. PEAP
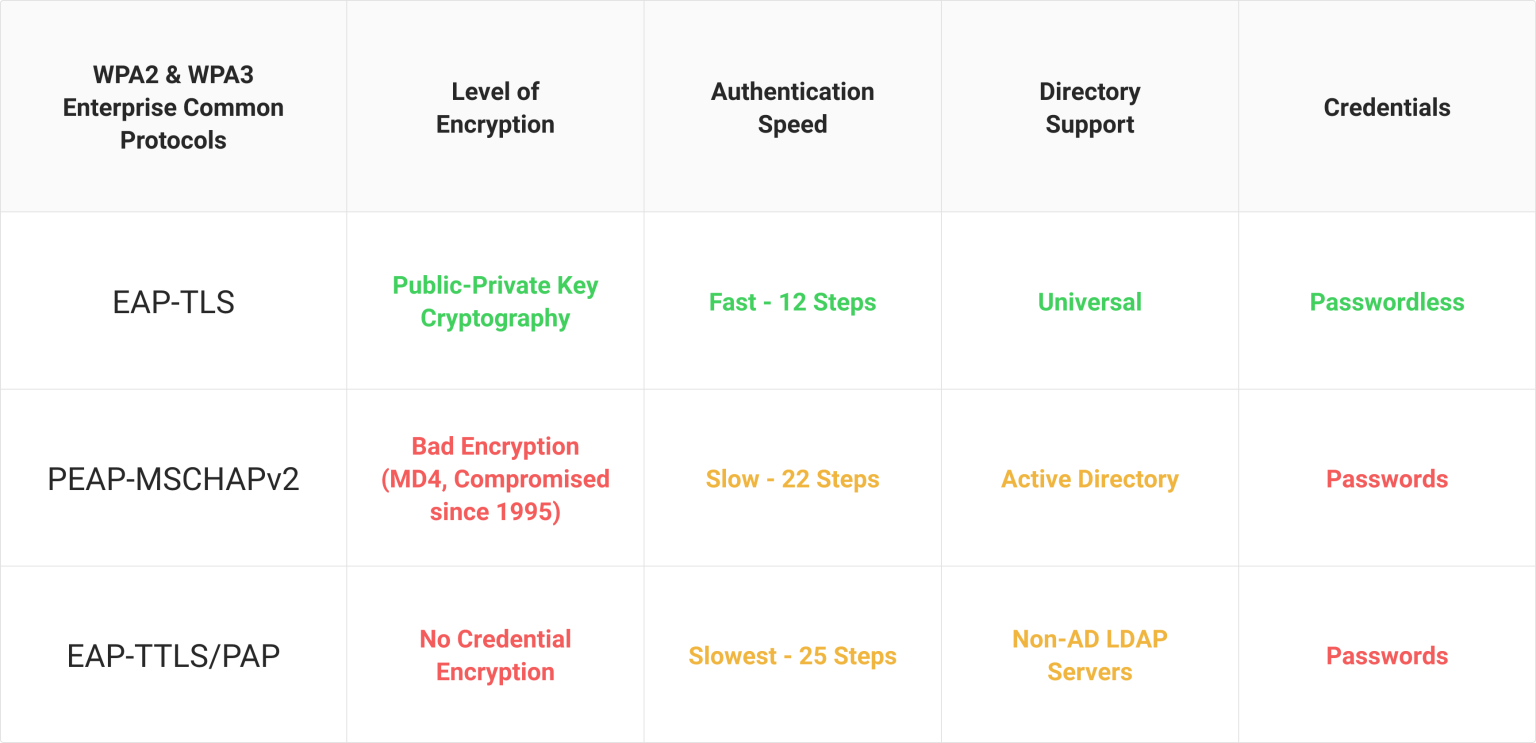
PEAP is a type of EAP that contains information for chaining multiple EAP mechanisms together for additional security. PEAP does not handle the authentication mechanism itself but acts as a wrapper for secure inner authentication mechanisms, like Microsoft Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol version 2 (MSCHAPv2). PEAP’s security level depends on the strength of the inner authentication mechanism, such as MSCHAPv2 or TLS.
PEAP-MSCHAPv2 is a popular PEAP configuration. It uses MSCHAPv2 as the authentication mechanism for credential verification. It relies entirely on password-based authentication and uses Active Directory in an on-premise setup. Using credentials makes PEAP-MSCHAPv2 highly susceptible to credential-based threats like Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attacks, ARP poisoning, and MAC spoofing.
Organizations, like small businesses and universities that find managing client certificates difficult can use PEAP to help balance security and ease of configuration.
EAP-TLS is the most secure 802.1x authentication protocol because it uses digital certificates for client and server-side authentication. Digital certificates use asymmetric encryption that uses a public-private key for authentication and identity verification.
Server Certification Validation is an integral part of EAP-TLS, where the client verifies the authenticity of the server. During the 1st stage, server verification, the server verifies and validates the client certificate before examining the CRL or certificate chain. Similarly, during client verification, the client verifies and validates the server certificate and examines the certificate chain afterward. After authentication, the client and server both generate a session key to encrypt data. Once the session key is set, the client and server can use the TLS channel to communicate securely.
EAP-TLS uses digital certificates, which reduces the risk surface that inherently comes with using credentials in PEAP-MSCHAPv2. EAP-TLS’s authentication speed is also relatively faster compared to other authentication protocols. Since it requires certificates to authenticate both client and server-side, it supports almost all the directories present in the cloud, such as Entra ID, Okta, Google, and others.
Going Passwordless With EAP-TLS
EAP-TLS and PEAP solve the issue of securing wireless communication but in contrast with the authentication mechanism and network infrastructure requirements. PEAP relies heavily on passwords, while EAP-TLS relies on certificates. Implementing EAP-TLS requires an efficient and managed Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) to automate and manage the entire lifecycle of certificates.
A dynamic cloud PKI with a Cloud RADIUS simplifies the onboarding process, eliminating the vulnerabilities of passwords and on-premise setups. This strengthens the EAP-TLS framework by providing superior integration with almost all Identity providers, such as Entra ID, Okta, etc. See how a university eliminated the risk of cyberattacks and network insecurity by shifting to the EAP-TLS authentication protocol.