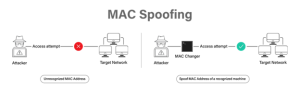
MAC spoofing is when an attacker tricks a network by faking a device’s unique ID (MAC address) to gain unauthorized access or disrupt communication. This attack can happen in different ways, like modifying the hardware itself, spoofing the identity of that device, tampering with messages, or capturing packets containing response data.
Learn more about different Wi-Fi hacks and effective ways to prevent them.
How Does MAC Spoofing Work?
MAC spoofing works by changing a device’s MAC address via software and allowing it to impersonate another device on the network. Hackers can accomplish this by employing software that changes the MAC address of their network interface card (NIC). These tools make the procedure quick and easy, frequently with only a few clicks.
Once the MAC address is changed, the network incorrectly recognizes the attacker’s device as the real one. This change allows the attacker to intercept data destined for the originating device.
What are the Potential Risks of MAC Spoofing?
- Unauthorized Network Access: Attackers evade MAC filtering and gain unauthorized network access by imitating a valid device’s MAC address.
- Data Interception: Data interception allows attackers to steal sensitive information, hijack sessions, and manipulate communications, leading to identity theft, financial loss, or data breaches.
- Network Disruption: MAC spoofing can disrupt networks by establishing unauthorized access points, restricting genuine users, and allowing attacks such as session hijacking. This can result in data breaches, service disruptions, and financial losses.
- Identity Theft: Identity theft may occur when attackers gain wireless network credentials and build unauthorized access points.
- Difficulty in Tracking Attacks: Attackers can disguise their devices, making identifying and preventing unwanted activity impossible.
How do you detect MAC Spoofing Attacks?
To identify MAC spoofing attacks, check your network traffic for strange patterns or several devices using the same MAC address. In addition, ARP tables should be looked at regularly for anomalies, such as several IP addresses associated with the same MAC address.
You should also use Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) to detect and warn you of spoofing attempts. Switches can be configured with port security to limit the amount of MAC addresses per port and shut off ports if spoofing occurs.
MAC Spoofing Attack Example
Let’s say a criminal is targeting a bank’s internal network. They first determine the MAC address of a genuine bank employee’s computer, which might be accomplished by network scanning or eavesdropping on unprotected Wi-Fi traffic. Once they have obtained this information, they change the MAC address on their device to match the employee’s.
Using this spoofed MAC address, the attacker gets over MAC filtering security mechanisms and gains unauthorized access to the bank’s internal systems. Depending on their intentions, they could:
- Intercept sensitive client data, such as account numbers, transaction history, and personal information.
- Manipulate financial transactions by posing as an authorized user of the payment system.
- Spread malware throughout the bank’s network, which might lock staff out of their computers.
- Create backdoors for persistent access, allowing them to return and abuse the system later.
This attack can result in financial losses, data breaches, and serious reputational harm to the bank.
How to Avoid MAC Spoofing Attacks?
These types of attacks are difficult to detect and avoid, but encryption reduces the risk by protecting network data. Even if an attacker obtains access using MAC spoofing, robust encryption makes it more difficult for them to view or alter important data.
You should use access control lists (ACLs) to restrict network access only to permitted MAC addresses and split the network into smaller subnets to minimize the potential spread of attacks. Improving port security by setting switches to allow only particular MAC addresses and utilizing Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI) to evaluate ARP requests and answers is also beneficial.
Make sure to use MAC address tracking tools to keep track of any strange or duplicate MAC addresses on your network. In addition, monitor your network traffic regularly for strange patterns. Authentication techniques should also ensure that only authorized devices connect to the network.
Prevent MAC Spoofing Attacks with SecureW2
SecureW2 offers advanced security solutions that let network administrators identify and verify people and devices using digital certificates, a more secure password alternative. SecureW2 protects the network by confirming a device’s identity, role, and compliance status.
SecureW2’s dynamic network segmentation reduces MAC spoofing vulnerabilities by preventing attackers from traveling laterally throughout the network. Even if a faked device obtains access, regulations can limit its scope based on role, device health, or security posture, reducing potential harm.
Furthermore, SecureW2 makes onboarding easier by allowing organizations to switch from weak or hacked passwords to certificate-based authentication, eliminating a popular attack vector for MAC spoofing and other security risks.
Contact us now to understand how our solutions can prevent MAC spoofing and other network attacks.