Network security is one of the important factors for organizations of different sizes. As cyber threats evolve, authorized access to network devices and critical resources becomes very important. Port-Based Network Access Control (PNAC) is an effective authentication method that helps achieve what we desire.
PNAC is closely linked to the 802.1X standard. This authentication framework guarantees that users must have unique credentials or certificates to access network resources, verified by an authentication server. By implementing PNAC, organizations can prevent unauthorized access and improve their security posture.
In this article, we’ll explore PNAC, how it works, and why it is essential for maintaining a secure and controlled access network. Whether you’re new to the concept or looking to strengthen your network security, this guide will provide valuable insights into Port-Based Network Access Control. Keep reading to learn more!
What is Port-Based Network Access Control (PNAC)?
Port-Based Network Access Control is a security mechanism that controls network access at the port level. By implementing PNAC, organizations can ensure that only authorized devices and users can connect to their infrastructure.
As we already discussed, PNAC is closely associated with the IEEE 802.1X standard, which provides a robust framework for authenticating network devices attempting to connect to a wired or wireless network. The 802.1X standard uses an authentication protocol that requires each user or client device to have unique credentials or certificates. An authentication server, typically a RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) server, validates these credentials.
PNAC is essential for maintaining a secure network environment. It helps prevent access to unauthorized devices by authenticating them before they access the network. By leveraging the 802.1X standard, PNAC provides an effective solution for network access control.
How Does Port-Based Network Access Control Work?
Port-Based Network Access Control operates in the following way:
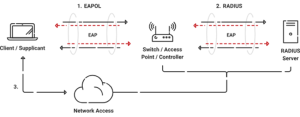
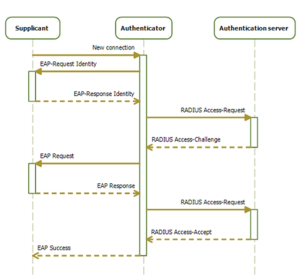
- Connection Initiation: When a client device connects to a controlled port, the authenticator detects the connection.
- Authentication Request: The supplicant sends an authentication request to the authenticator. Then, the authenticator forwards it to the authentication server.
- Validation: Authentication servers validate the credentials or certificates provided by the supplicant.
- Access Decision: If the credentials are valid, the authentication server instructs the authenticator to grant network access to the supplicant. If the credentials are invalid, access will be denied.
Figure: Thanks to Wikipedia
What Other Security Protocols Does PNAC Use?
PNAC is often integrated with other security protocols to provide a robust network security solution. These networking protocols enhance the overall security posture of an organization. Here are some of the key security protocols commonly used in conjunction with PNAC:
RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) or Authentication Server
RADIUS is a central component in the PNAC framework. It is the authentication server that verifies the credentials of users or devices attempting to access the network. The RADIUS server authenticates, authorizes, and accounts (AAA) for users, ensuring that only legitimate access will be granted. It supports password-based and certificate-based authentication, making it more secure.
EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol)
EAP is an authentication framework frequently used in wireless networks. It is used within the 802.1X standard to provide various authentication methods, such as EAP-TLS (Transport Layer Security), EAP-TTLS (Tunneled Transport Layer Security), and PEAP (Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol). These methods enable secure transmission of authentication information, ensuring that valid credentials are used during the authentication process.
LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol)
LDAP is used to access and manage directory information services over an IP network. In the context of PNAC, LDAP can be integrated with the authentication server to retrieve valid credentials and other authentication-related information from a centralized directory, such as Microsoft Active Directory (AD). This integration allows for streamlined user management and supports mission-critical applications.
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)
SNMP is used for network monitoring. In conjunction with PNAC, SNMP can monitor network access and client device status, allowing network security engineers to detect and respond to unauthorized device access.
Network Access Control Lists (ACLs)
ACLs are used to define rules that control the incoming and outgoing traffic. With PNAC, ACLs can enforce access control policies, allowing or denying traffic to access network resources. This fine-grained control helps protect sensitive data and network assets from unauthorized device access.
What Can You Do with 802.1X Authentication?
802.1X authentication offers various functionalities that enhance network security and manageability. Here are the key capabilities that 802.1X authentication provides:
- Pre-Admission Control: Blocks unauthenticated messages, ensuring that only devices and users with proper credentials can initiate a connection.
- Device and User Detection: Identifies users and devices based on predefined credentials or machine IDs, enadevicewirebling precise control over network access.
- Authentication and Authorization: Verifies user or client device credentials and the authentication server determines whether to grant access to the network, ensuring that only authenticated entities can connect.
- Centralized Authentication: 1X authentication enables centralized authentication via an authentication server, typically a RADIUS server. Centralized authentication makes user management easier and provides uniform authentication policies across the network.
- Profiling: Scans connected devices to gather information about compliance status, which helps enforce security policies.
- Policy Enforcement: Applies role-based access control policies, ensuring users and devices access only authorized resources.
- Post-Admission Control: Enforces session termination and cleanup processes, ensuring that sessions are properly closed and resources are freed when access is no longer required.
By leveraging these capabilities, 802.1X authentication provides a comprehensive solution for securing network access and ensures that only authorized devices and users can connect. Configuring devices for 802.1X networks can be challenging. However, with the right onboarding technology, this can be overcome; we provide a self-service onboarding application for unmanaged devices as well as gateway APIs to automatically configure managed devices for certificate-based authentication.
Problems 802.1X Network Access Control Addresses
The presence of social media, cloud computing, and BYOD policies in daily and business life has significantly impacted enterprise network resources. This has led to increased productivity but also increased exposure to network threats. Implementing 802.1X Network Access Control provides an answer to these challenges by ensuring network access to only authorized devices and users. This authentication is essential in highly mobile environments where you can effectively reduce the risks associated with BYOD by enforcing strict device and user verification.
802.1X NAC also helps manage the increased network traffic from social media and cloud computing by controlling access at the network ingress point. This reduces the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected. Also, 802.1X’s centralized authentication system improves network management, reduces total cost of ownership (TCO) by eliminating the need for additional security measures, and avoids security risks. 802.1X NAC addresses these critical issues, allowing organizations to maintain a secure and resilient network environment.
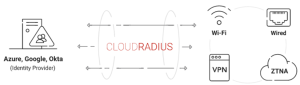
Using Certificate-Based Authentication with Cloud RADIUS to Implement 802.1X
Port-Based Network Access Control (PNAC) provides an excellent basis for ensuring that only authorized devices and users can access your network. Using the IEEE 802.1X standard, PNAC improves security and simplifies network administration, making it a crucial component of any organization’s security strategy.
SecureW2’s Cloud RADIUS provides a robust and passwordless authentication solution that uses certificates to enhance network security. By employing digital certificates instead of traditional passwords, Cloud RADIUS reduces the dangers of credential theft and unauthorized access, which is critical for 802.1X systems that require safe and quick authentication. Certificate-based authentication requires a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), and SecureW2 offers a fully managed cloud PKI solution that contains everything needed to deploy passwordless authentication. Our PKI and Cloud RADIUS function flawlessly with all network infrastructure forms, including significant IDPs, MDMs, and wireless access points.
Contact us today to find out how SecureW2 can assist you in implementing PNAC and safeguarding your critical assets.