Key Points
- Common Wi-Fi security concerns include man-in-the-middle attacks and password cracking, frequently targeting weak Wi-Fi credentials.
- Wi-Fi protocols such as WEP, WPA, WPA2, and WPA3 specify network security standards. WPA2 and WPA3 offer far greater protection than older WEP and WPA protocols, particularly in enterprise environments.
- Improve Wi-Fi security by changing passwords, enabling firewalls, and using certificate-based authentication.
Wi-fi networks are ubiquitous as more and more users connect to networks remotely for work, access data and applications, and manage IoT devices. As their popularity grows, so do the associated risks, as cyber-attacks are increasing rapidly. A leading security researcher has published a paper on the vulnerability of a password-protected wi-fi network. This vulnerability could expose almost 2.3 billion users worldwide to a clone of their wifi network. A rogue wi-fi network can intercept traffic and expose data and users to data theft.
Understanding the vulnerabilities of a misconfigured wi-fi is the first step toward securing your devices and users. Attacks like MITM, brute force attacks, phishing, evil twin attacks, and packet sniffing can all be mitigated with the proper knowledge and precautions. This article aims to equip you with this crucial knowledge, empowering you to protect your Wi-Fi for secure connectivity.
Different Attacks that Could Hack into Your Wi-Fi Network
If you are an organization with many managed and unmanaged devices and users, you must understand and mitigate the risks of wifi attacks on your network. Here are some attacks that could easily compromise the security of your wi-fi network through attacks like
- Man in the Middle Attacks
- Evil Twin Attacks
- MAC Spoofing
- Packet Sniffing
- Brute Force Attacks
Man-In-The-Middle (MITM) Attacks
As the name suggests, a Man-In-The-Middle attack is when an impostor positions himself between a user and a network through a rogue access point, intercepting and potentially altering the communication. This attack can go unnoticed, allowing the attacker to eavesdrop on sensitive information or manipulate the transmitted data.
MITM is orchestrated by spoofing an SSID, where a rogue access point is set in the same Wi-Fi network as the legitimate SSID. This makes users believe they connect to the genuine SSID and impart their information. The consequences of falling victim to an MITM attack are financial and reputational, as users and business organizations suffer significant monetary losses and have their names and credibility maligned. It’s crucial to be aware of these risks and take necessary precautions.
Evil Twin Attacks
An evil twin attack occurs when a user is led to connect to a rogue wi-fi access point set up by the attacker. As a user connects to a rogue wi-fi access point, any data they share can be accessed as it passes through the server set up by the attacker. They are common on public, unsecured wi-fi networks, leaving your data vulnerable.
To conduct an evil twin attack, the attacker looks for a proper location with multiple access points having the same name. Then, he sets up a similar account with the identical SSID and uses a device called the wi-fi pineapple for a border range. He moves closer to the victim and creates a fake captive portal to capture login credentials. Once this is done, the hacker can access the credentials and use them to steal and control the network.
MAC Spoofing Attacks
MAC spoofing is one of the oldest spoof attacks. It uses the flaws in MAC authentication bypass to attack a network. A MAC attack is pretty easy to orchestrate, as it depends on the device’s MAC address (the number identifying a machine) and can be changed easily.
MAC spoofing provides unauthorized access to an attacker by letting him configure an access point to capture user credentials. Thus, disabling unnecessary ports or firewalls to protect your network is always advisable.
Packet Sniffing
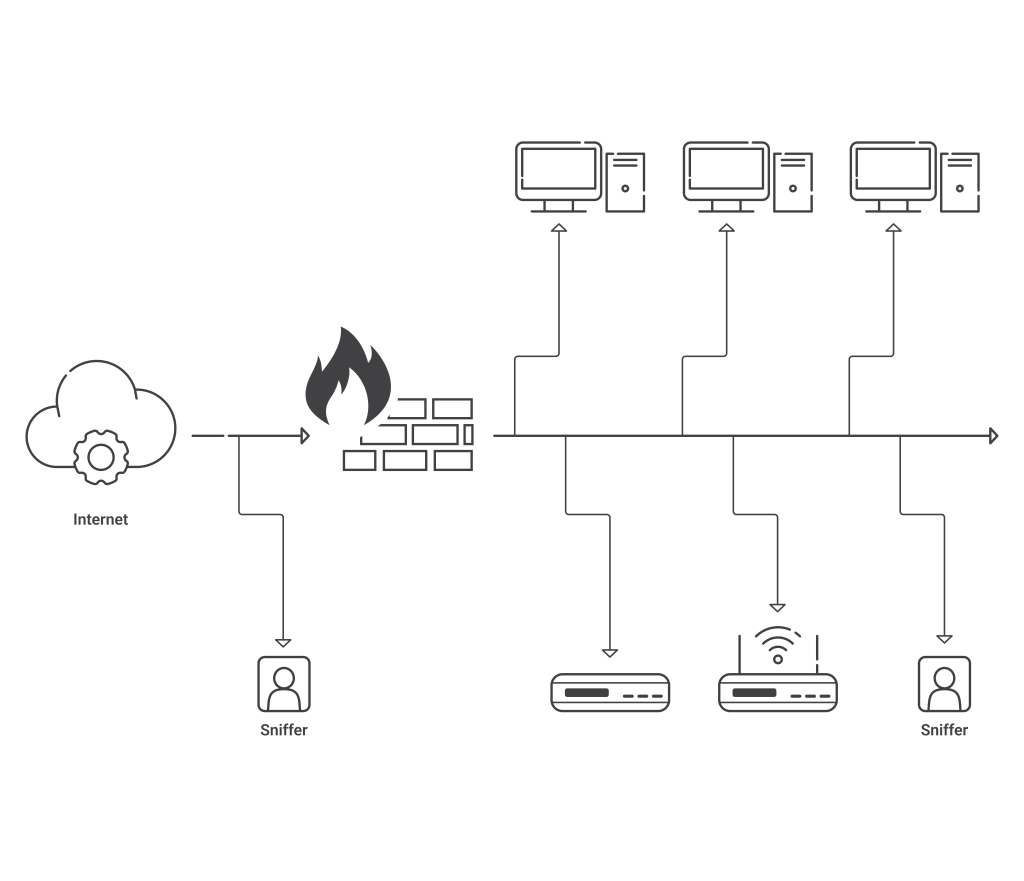
A “packet sniffing” attack occurs when a hacker collects data packets, mainly on an unprotected network. A packet sniffer collects information like login credentials, financial information, and other sensitive data and sells it to unscrupulous elements for further attacks. Once a hacker gets access to this information, he can log in to your accounts to further their attacks and gain control over your network.
A sniffing attack works best on unprotected networks. It is always advised to use VPNs on an unprotected network. As a user, you should also be careful to check the website certificate and always use safe and trusted websites before sharing credentials.
Brute Force Attacks
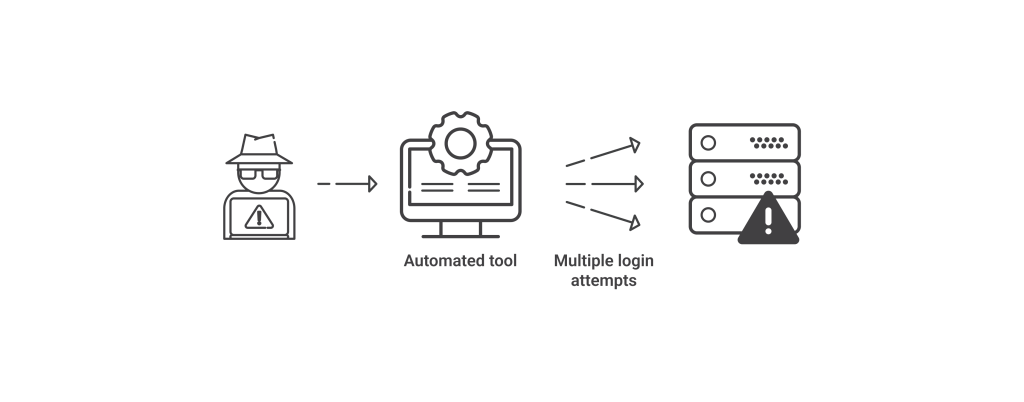
Brute-force attacks try to guess credentials like usernames and passwords using tools that try different combinations of credentials to steal sensitive information. Most of the time, highly successful bots carry out brute-force attacks successfully. A dictionary attack is a popular brute-force attack in which the words in a dictionary are used to find a password. They can be combined with numbers and special characters to crack more complex passwords.
Another popular brute force attack is the credential stuffing attack, where the attacker uses stolen credentials and stuffs them into login forms to see if they work. These credentials are sold on the dark web and are usually successful when users use almost the same passwords for different accounts.
How to Protect Your Wifi Connection From Attacks?
When a wi-fi network is unsecured, it can be easily accessed by any user or device nearby and can prove hazardous to the organizational network. A hacker can use the network to gain access to personal information identities, compromise sensitive data, and try to listen to secure communications.
One of the foremost ways to avoid hacking attempts and secure your wi-fi is to change the default password on all your network devices. Any Wi-Fi device is equipped with an admin password to set up the device, and it can be easily cracked. So, changing passwords frequently with complex ones is a necessity. Here are some ways to protect your wi-fi from further attacks:
- Use MAC Address Filtering To Secure Your Network
- Use VPN to Encrypt Wi-Fi traffic
- Wi-Fi Encryption to Enable Robust Wireless Network Security
- Secure Users and Devices With Passwordless Solutions
Use MAC Address Filtering to Secure Your Network
A MAC address is a unique identifier for a device. It is a twelve-digit hexadecimal number used to identify desktops, laptops, mobile devices, or a wireless local area network (LAN). MAC address filtering provides access control to devices with a particular MAC address, thus limiting the number of devices that can access the network.
A wireless router will provide access to a device if the MAC address matches the list; otherwise, access is denied. In MAC address filtering, the router has a list of approved and denied devices, thus preventing unauthorized access and filtering out unknown devices.
Use VPN to Encrypt Traffic
A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, protects your Wi-Fi from unauthorized access and hacking attempts. It lets a user create a secure tunnel protected by their identity. A VPN also hides the user’s IP address and masks the data passing through the VPN server with a virtual IP address, thus protecting the real identity and preventing credential theft and hacking attempts.
Wi-Fi Encryption to Enable Robust Wireless Network Security
Another way of protecting your wi-fi network is by utilizing wi-fi protected access (WPA) protocols that encrypt your messages as they travel from the wireless connection to the server. Some Wi-Fi protocols have been used, such as WPA and WPA2. The WPA2-PSK is a commonly used wi-fi protocol, but it uses pre-shared keys that double the risk of credential theft and hacking on a network.
The WPA2-Enterprise is considered the gold standard in wi-fi protocol as it supports EAP-TLS and digital certificates for authentication.
Secure Users and Devices with Passwordless Solutions
Using passwords to secure your network has proven ineffective, as they are vulnerable to phishing attacks. Organizations like the NIST are recommending passwordless solutions like MFA and digital certificates for a robust wi-fi security solution. MFAs are still vulnerable to social engineering and phishing attacks, but digital certificates are widely used as they are based on the principle of asymmetric cryptography.
Digital certificates are phishing-resistant and tied to specific users and devices. Thus, they cannot be stolen or duplicated. A managed PKI and an onboarding solution make managing certificates easier and are highly recommended for large organizations.
How Do You Configure Secure Wi-Fi Settings on Managed Devices?
An internet connection is a foremost need for devices connecting to a corporate network. The wi-fi credentials are shared with many users and devices, which may lead to unauthorized access to the network. Users may sometimes connect to public Wi-Fi, leaving their managed devices vulnerable to data breaches. A safe way to connect managed devices to a wireless network is necessary. As an admin, here are some steps to accurately configure a device’s wi-fi settings:
- Go to your MDM console and click on Device mgmnt> Profiles. Create a new wi-fi profile based on your existing OS.
- Select Wi-fi from the list of supported policies.
- Enter the SSID of the Wi-Fi you want your device to connect to.
- Click on Connect to this wi-fi automatically. This ensures your device is connected to the specific wi-fi only, not any other rogue SSID.
- Make sure the wi-fi connection is hidden and not detectable.
- Select the Security type and enter the required details. This ensures the user is not prompted to enter credentials while connecting to the wi-fi. You can also configure a proxy for wi-fi configuration.
- Save and publish the wi-fi profile and test with a single device before applying group policies.
Use SecureW2 to Secure Your Network With Passwordless Solutions.
The Wireless Fidelity Alliance allows you to connect to wireless routers to a wireless access point through wi-fi-protected access (WPA). It certifies wi-fi products for safe and secure connections of managed and unmanaged devices to your network. Passwords have repeatedly proven ineffective in securing a wireless network as they are prone to attacks. Digital certificates protect your wireless networks from attacks like phishing and MITM as they are phishing-resistant. However, certificates should be managed with a PKI, which can be cumbersome and time-consuming. A managed Gateway API like SecureW2s JoinNow Connector PKI and JoinNow MultiOS protects your wireless network from unwanted attacks and events.
Our Managed Gateway API integrates with your existing infrastructure and popular MDMs like Intune and Jamf. It effectively manages digital certificates and is equipped with auto revocation policies (for Jamf and Intune only), so you can set the policies and be at peace, as your wireless network is now managed securely.
Click here to learn about our passwordless solutions today.