Did you know that the cost of data breaches reached a whopping $4.35 million in 2022? Data breaches cost organizations a lot in penalties and lost business opportunities. Almost 68% of organizations that had suffered a breach had to increase product and service costs, making it difficult to get new business.
With the internet constantly evolving, there has been growth in computer networks too. Organizations are now accessing more data and information through their network, making them more susceptible to breaches, hacks, and cyberattacks than ever before. As a result, network access control in security is paramount in running a successful business.
Modern cybersecurity tools comprise a combination of network security solutions like network access control applications, configuration management, and tools used to manage a network effectively. An effective network security strategy is like a gatekeeper, preventing unauthorized access, Layer 2 attacks, and phishing attempts.
However, a significant aspect of network security often overlooked is 802.1X port security. If the ports are not secured well, they could wreak havoc through Layer 2 attacks and even take complete control of your network.
Read on to learn more about the 802.1X port security protocol and how it provides port-based network access control to secure your network.
What Is a Port?
A port is a virtual point in a network where a connection starts and ends. Every port is related to a process or service. A computer can distinguish between the various kinds of traffic. An email goes to a port different from webpages, though they have the same destination on the network and are routed through the internet connection.
What Is a Port Used for?
A port is used for:
- Networking
- Security Hardware
- Computer Software
Networking
In networking, a port has a predefined set of numbers for guided communication. The port on your device allows for communication by facilitating the reception and transmission of packets for an enumerated service. An email would have specific ports different from web pages, for example.
Computer hardware
Ports also provide sockets to plug in a USB or an Ethernet cable to establish a connection to the Layer 2 of your network.
Software
A port is dedicated to converting software to work on hardware or an OS different from its original purpose.
What Is 802.1X Port Security?
The IEEE 802.1X standard is an authentication protocol for port-based network access control. It provides an authentication mechanism for any device that needs to connect to a LAN or a Wi-Fi LAN. IEEE 802.1X authentication has three parties involved in the authentication process: the user, the authenticator, and an authentication server.
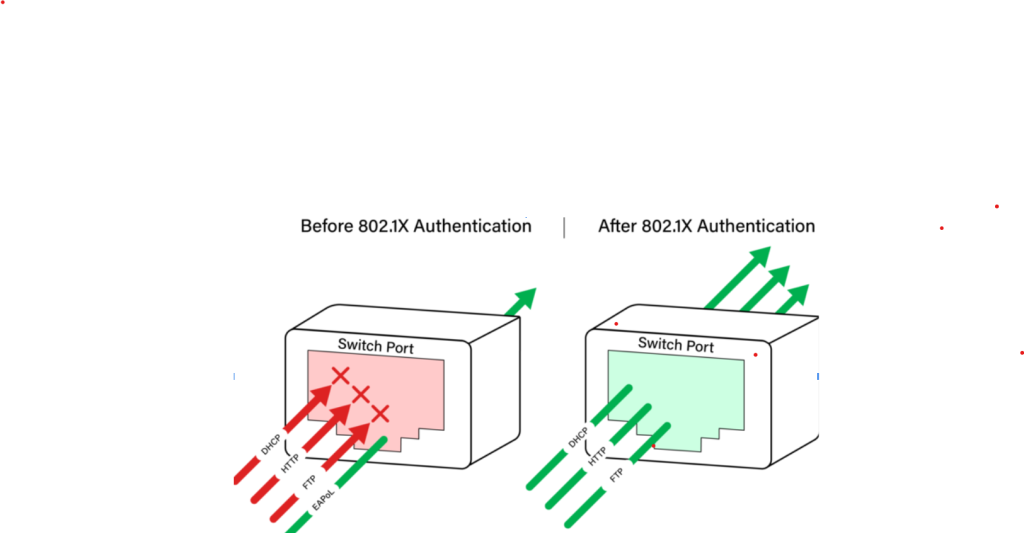
The Authentication servers run software that supports the RADIUS and the EAP Protocols. Users can authenticate themselves through credentials or a digital certificate on the RADIUS server. The RADIUS server can communicate with the organization’s directory, typically over the LDAP or SAML protocol.
How Does the 802.1X Protocol Work?
- A supplicant, i.e., the user or device, places a request to be authenticated to the network. The request is put to an authenticator, typically a network switch or an access point.
- The authenticator transmits an Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) request to the supplicant. The request accommodates an identity verification asking the supplicant for credentials to identify themself.
- The user (supplicant) supplies their identity, like username, password, or certificate, for further authentication.
- The authenticator asks for another EAP request for further authentication of the supplicant.
- The supplicant responds by sending a password, token, or any other form of credential.
- The authenticator forwards the newest credential for verification to the authentication server.
- The authenticator verifies the credential and responds with an indication to authenticate or refuse authentication.
- Upon the response, the authenticator grants or denies access to the supplicant onto the network.
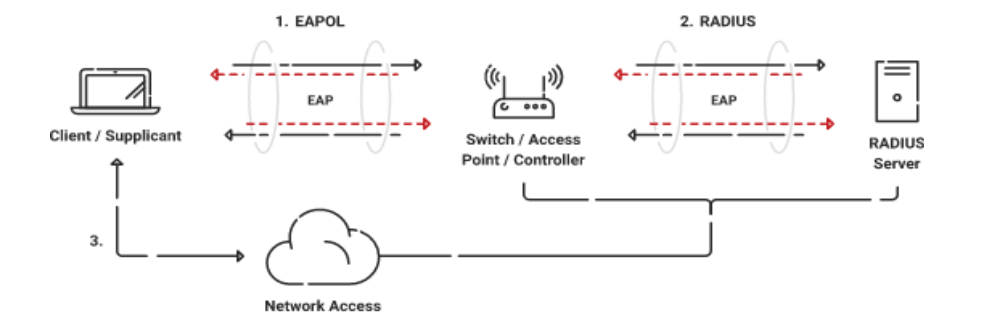
Working protocol
What Is 802.1X EAP Security?
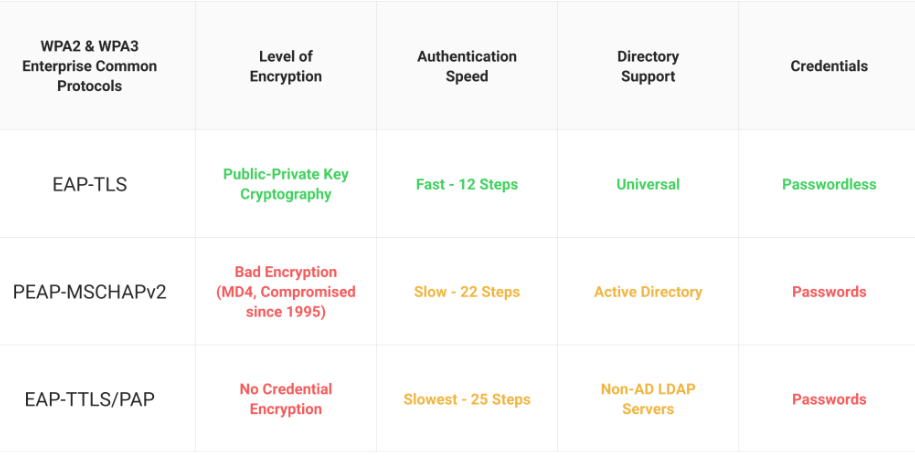
The IEEE standard authentication protocol widely used on encrypted networks is the Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP). EAP is a secure form of sending user information on air for network authentication. 802.1X is the standard for relaying EAP through wired and wireless Local Area Networks (LAN). The EAP tunnel is encrypted, thus mitigating outside threats and hackers from intercepting any information.
The EAP protocol can be deployed for credentialing (EAP-TTLS/PAP and PEAP-MSCHAPv2) and digital certificate (EAP-TLS) authentication. It is considered the safest and most secure for protecting the authentication process.EAP-TLS is a protocol that supports the use of client digital certificates. Digital certificates provide superior security compared to passwords as they rely on public key-private key encryption to send data over the air. They also use EAP-TLS, the gold standard for authentication.
How Does 802.1X Authentication Protocol Secure Your Network?
The 802.1X protocol ensures that users interacting with the network are who they say they are. It acts as a gatekeeper between the supplicant and the network. To secure a network, 802.1X performs the following functions:
- Pre-admission control
- Device and user detection
- Authentication and Authorization
- Policy enforcement
- Post-enrollment control
Pre-admission Control
802.1X authentication mitigates the risk of attacks by preventing any unauthorized messages on the network. It prevents hackers that may try to attack the network by brute force.
Device and User Detection
By implementing the 802.1X protocol through a Cloud-based RADIUS, an admin can issue specific credentials in the form of passwords or certificates to the intended user. Password and digital certificates limit the access group to a trusted number of users and prevent unauthorized access.
Authentication and Authorization
The 802.1X protocol offers port-based authentication wherein the Media Access Control (MAC) service provides a secure connection between the user and the network. The MAC layer in a network is responsible for transmitting data packets from one interface to another.
Policy Enforcement
802.1X allows an admin to create access policies to the network based on specific roles, permissions, and attributes. Role-based access control and attribute-based access control enforce policies based on user profiles and attributes in a network.
Role-based access control ensures unauthorized users cannot access protected information or data, e.g., personnel from the human resources department cannot access engineering codes and vice versa.
Attribute-based access control sets policies based on popular user attributes like user location, session duration, typical login time, etc.
Benefits of the 802.1X Authentication Protocol
The 802.1X protocol is tried and tested and has been running and providing network security globally for ages. It has been the de facto standard for network authentication since the early 2000s. 802.1X offers the following benefits:
- Scalability features
- Robust security
- Vendor agnosticism
Scalability
The 802.1X protocol is a highly scalable and versatile authentication protocol. It can support many Cloud RADIUS servers, multiple server profiles, and a combination of authentication policies. It provides authentication for wired and wireless networks. It also allows for authentication through digital certificates.
Robust Security
The 802.1X protocol has a firm security profile. It can be configured with EAP protocols like PEAP-MSCHAPv2, EAP-TLS/PAP, and EAP-TLS. These provide a more robust security mechanism to send information and data securely over the air.
EAP-TLS, along with the WPA2-Enterprise, is considered the gold standard for network security as it is the only protocol that exclusively supports digital certificates for authentication.
Vendor Agnosticism
802.1X is an industry standard for Wi-Fi authentication by the IEEE and has been in practice for a long time. As a result, most devices on the market have an 802.1X supplicant if they are expected to connect to Wi-Fi. Some devices, like printers and IoT devices, have third-party options to load a supplicant.
802.1X is a well-documented, highly scalable, and vendor-agnostic protocol. However, there are a few drawbacks to the 802.1X protocol. Those drawbacks include the following:
- Complex to configure
- Chances of misconfiguration
- Expensive to scale
- Challenging to manage unmanaged devices/BYOD
Complex to Configure
802.1X requires a complex switch port configuration process for every device. An organization keeps adding users and devices to the network, making configuration cumbersome and leading to more misconfiguration. Misconfiguration of devices leaves your network vulnerable to MITM and other Layer 2 attacks.
Higher Chances of Misconfiguration
802.1X is generally secure but still prone to vulnerabilities if not properly configured. The security of 802.1X depends solely on the network policies created within an organization. If a network requires a mere password to gain access, then the network can be compromised through dictionary attacks and Man-In-the-Middle attacks.
Expensive to Scale
Legacy network ports do not support the 802.1X authentication protocol, and changing all legacy network setup appliances to 802.1X would be costly. However, a Cloud RADIUS solution like SecureW2’s JoinNow Cloud RADIUS is a cost-effective cloud-based RADIUS solution.
The Cloud RADIUS solution is designed to provide zero-trust, passwordless network authentication without a complicated setup. A dedicated support team ensures the RADIUS is set up seamlessly so you can start issuing certificates immediately.
Cloud RADIUS is also inexpensive compared to the legacy on-premise RADIUS servers, as you don’t have to worry about setting it up on every premise separately. Additionally, Cloud RADIUS is cloud-based and can authenticate your whole network from the cloud.
Does a Network Need 802.1X Authentication?
The answer is simple: yes.
Your network needs 802.1X authentication right away. It provides a robust network security protocol that has been tried and tested for efficacy for years. Strong network authentication is essential with a monumental rise in unmanaged and BYOD devices. 802.1X port-based network access control (PNAC) enables authentication for any device or user connecting to the network.
The strength of PNAC is dependent on the wireless protocol in use. The EAP-TLS wireless protocol is the best EAP security solution in the 802.1X protocol. The EAP-TLS protocol uses simple public-private keys to achieve symmetric cryptography. It also uses server certificate validation to complete the authentication and ensure that the user is not a victim of a MITM attack.
Use SecureW2’s Passwordless Solutions for Robust 802.1X Security.
You may wonder why you should secure your network as everything is stored on the cloud, thus keeping all your data safe. Securing information on the cloud alone is insufficient to secure your network. A fully secure environment can be achieved only when you secure hardware, software, and all the ports on your network.
SecureW2’s Cloud RADIUS increases control of your network. It provides overall visibility of all the devices and users on your network. Being vendor-neutral, it can easily integrate with major identity providers to do real-time look-ups during authentication for network policy implementation.
Cloud RADIUS supports MAC Auth Bypass for IoT devices that do not support 802.1X configuration, thus bringing these devices under network visibility that would otherwise have gone unmonitored.
Click here to learn more about pricing.

