Key Points
- To secure your network,you need to follow effective RADIUS accounting practices, such as role-based access control, frequent data backups, encryption, monitoring, and clearly stated retention policies.
- By using strong encryption, ongoing monitoring, and deliberate data retention, you can ensure that confidential information is kept safe and network performance is preserved.
- With our cutting-edge Cloud RADIUS, you can simplify network management and security while effortlessly incorporating best practices through an intuitive gateway.
RADIUS is a crucial networking protocol best known for centralized authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) administration. The final “A” in AAA signifies accounting, a fundamental aspect of network management. Network Access Servers (NAS) typically function as clients and manage user access, whereas RADIUS servers handle authentication and authorization.
Accounting in the RADIUS architecture aids network monitoring, user billing, and statistical analysis. The administration of RADIUS accounting data necessitates the implementation of a number of best practices. Effective accounting data management requires assuring data accuracy, preserving data integrity, and protecting sensitive information. Accounting data must be protected from unauthorized access and manipulation by implementing stringent security measures. Regular audits and evaluations of accounting records aid in identifying anomalies and ensuring network usage policies are adhered to.
In the image below, a RADIUS server has been configured alongside a dedicated database server (lower right) for the user accounting portion of “RADIUS accounting.”
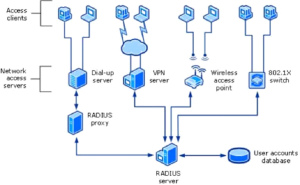
A RADIUS Server Setup with a Dedicated Server for User Accounting
How Does RADIUS Accounting Work?
The Radius AAA accounting procedure primarily commences when a user gains server access. The NAS then transmits a RADIUS Accounting-Request payload to indicate that the user’s network access has begun.
NAS devices act as clients in the same client-server architecture. User accounting data is sent by the NAS to a RADIUS accounting server. This accounting server saves user activity and network use data. RADIUS accounting tracks user sessions, data use, and other important parameters to measure resource consumption and ensure proper user invoicing.
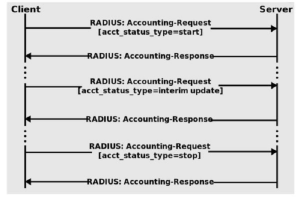
The RADIUS accounting process follows three overall steps:
- Accounting Start
- Accounting Request
- Accounting Stop
We’ll cover each of the phases in more detail below.
Accounting Start
When the NAS grants users access, the RADIUS server sends an accounting start transmission. Overall, this signifies the beginning of the user’s network access. In the packet transmitted by the NAS, an Acct Status Type attribute with the “start” is present. After that, it contains additional information, such as the user’s identification, network address, attachment point, and a unique session identifier.
Accounting Request
The NAS intermittently transmits These Interim Update records to the RADIUS server. These packets contain an “interim-update” value for the Acct-Status-Type attribute. In addition, the purpose is to inform the host of the present status of an active session, as well as its duration and data usage.
Accounting Stop
The NAS transmits an “Accounting Stop” record when the user is finished and the access is terminated. This transmission contains an Acct-Status-Type attribute with the value “stop” It includes details about the eventual usage. For instance, the amount of time transpired, the number of packets transmitted, the cause for the disconnection, and other data regarding the user’s network access. The RADIUS server stores all session-related data in a secure location.
Best Practices for RADIUS Accounting
1. Employ Role-based Access Control
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) provides a customized method for granting permissions by classifying users into distinct roles based on their responsibilities and duties. This practice ensures that users are equipped with the exact level of access required to complete their tasks, minimizing superfluous exposure to sensitive data and substantially reducing the risk of unauthorized data breaches.
RBAC provides a dependable mechanism for fine-tuning user permissions within RADIUS accounting. Consider a scenario where administrators, network operators, and auditors have distinct responsibilities. RBAC grants administrators comprehensive access to configuration settings, user data, and system records, facilitating effective system administration. The permissions of network administrators, who are primarily concerned with day-to-day operations, could be restricted to session management and troubleshooting tools, while auditors would have only read-only access to accounting logs for compliance audits. This nuanced access allocation improves security and streamlines workflows by removing the need for exhaustive permissions irrelevant to particular tasks.
It is essential that RBAC adheres to the principle of least privilege. The potential repercussions of security violations are drastically reduced by granting only the minimum access required to fulfill each role. In addition to reducing security risks, RBAC simplifies access administration by centralizing permissions and providing a consistent user access structure. Access modifications are automatically aligned with specified roles, which facilitates accommodating personnel changes such as new employees or role transitions. Ultimately, RBAC improves the RADIUS accounting practice by ensuring that users interact with data and features in accordance with their responsibilities, thereby enhancing security, accountability, and overall operational efficiency.
2. Regular Backup of Accounting Data
Accounting data must be backed up regularly to ensure that important information is safe and available in case of data loss, system breakdowns, or other unplanned events. RADIUS Accounting data gives useful information about user sessions, network usage, and bills, so businesses need to have a strong backup plan.
Accounting data that is backed up regularly acts as a safety net, protecting the organization from possible data loss disasters. By stressing the importance of regular backups, businesses can enjoy the following benefits:
- Data Protection: Backups keep you from losing data if you delete it by mistake, your system crashes, hardware breaks, or anything else that could cause data loss.
- Business continuity: When data is lost or a system fails, having up-to-date backups keeps the network running and minimizes downtime.
- Compliance and Auditing: Regulatory rules often demand that financial data be kept for a certain time. Regular backups make it easier to meet legal standards and audits.
- Disaster Recovery: Data backups are an important part of the organization’s disaster recovery plan in case of a big disaster or security breach.
- Accurate Billing and Reporting: Accounting data that is backed up ensures that bills and reporting processes are correct and reliable, keeping customer and shareholder trust.
3. Implementing Data Encryption
Data encryption is the most important part of RADIUS AAA Accounting because it makes sure that secret information sent between the RADIUS server and other network components stays private and safe. Encryption keeps accounting data safe from people who shouldn’t be able to see it and stops possible data leaks. Let’s look at the encryption ways that are good for sending data securely:
- AES (Advanced Encryption Standard): AES is one of the safest encryption standards available. It is appropriate for securing RADIUS Accounting data because of its robust encryption with key lengths of 128, 192, or 256 bits.
- TLS (Transport Layer Security): When sending sensitive information across a network, TLS is often utilized. When TLS is used with RADIUS Accounting, all data sent between the RADIUS server and clients is encrypted in transit.
- IPsec (Internet Protocol Security): IPsec is a group of technologies that allows for encrypted IP traffic. This allows for the secure transmission of RADIUS Accounting information across a network.
- EAP-TLS (Extensible Authentication Protocol-Transport Layer Security): To ensure the safety of RADIUS Accounting across wireless networks, EAP-TLS uses TLS-based mutual authentication and encryption. EAP-TLS also uses certificate-based authentication, which improves security by validating the identity of the RADIUS server and the users connecting to it.
4. Monitoring and Auditing
Maintaining network security and data accuracy requires constant monitoring and auditing of RADIUS accounting data. Organizations may maintain compliance with industry laws and prevent accounting problems by regularly monitoring the process.
Cloud RADIUS provides a filterable and easy-to-understand event logging system. This intuitive interface allows administrators to quickly analyze logs to pinpoint problems, reallocate scarce resources, and tighten network security. With Cloud RADIUS, organizations can easily monitor and protect their networks thanks to detailed event logs that allow for proactive RADIUS AAA Accounting system management.
Recommended Monitoring Tools and Practices
- Network Monitoring Software: Monitor RADIUS traffic, keep tabs on usage, and spot any suspicious activity with the help of network monitoring tools.
- Log Analysis Tools: Log analysis software should be used to examine accounting logs for red flags that might indicate security breaches.
- Real-time Alerts: It is recommended that administrators set up automatic alerts to be notified immediately of any crucial occurrences or suspicious actions.
- Regular Auditing: Verify the correctness and consistency of accounting data by performing regular audits.
- User Activity Tracking: Keep an eye on what they are up to so you can stop any shady dealings from happening.
- Integration with SIEM: Use Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems to analyze RADIUS AAA Accounting data for a full security picture.
- Data Retention Policies: Maintain necessary documents for audits and compliance by enforcing a data retention policy.
- Penetration Testing: Frequent penetration testing should be performed to find security flaws and evaluate the efficiency of monitoring controls.
5. Retention Policies for Accounting Data
Accounting data retention standards must be clearly defined to ensure efficient data management and regulatory compliance. Accounting data retention rules consider legal and regulatory constraints, business requirements, and data consumption to establish how long certain accounting records should be kept. Organizations may reduce their storage footprint and improve their ability to handle accounting data by establishing clear retention standards.
Importance of Defining Retention Policies
- Compliance and Legal Requirements: Regulatory bodies must often keep accounting records for a while. Setting up retention policies ensures that business rules and legal obligations are met.
- Data Usage and Analysis: How data is stored should match how it will be used. Keeping data only for as long as it is useful makes it easier to do worthwhile research and reduces the amount of data that needs to be stored.
- Data Security and Privacy: The danger of data exposure and unauthorized access to private financial information can be reduced with the right-keeping rules.
- Storage Optimization: Organizations can make the best use of their storage space and reduce data costs by deciding how long to keep data.
- Effective Data Purging: Well-defined keeping policies make it possible to eliminate old or useless accounting data on time, making room for more important information.
Network Management with Data Enrichment Services (DES)
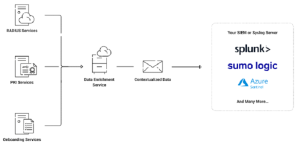
The Data Enrichment Service (DES) from SecureW2 is a seamless way to improve your network management capabilities. DES assures the seamless transmission of event logs and records from SecureW2 to your servers, allowing you to comply with regulatory requirements by retaining data for as long as necessary. This comprehensive data retention and maintenance strategy is required for effective accounting procedures.
DES enables you to better understand your network by contextualizing alarms across platforms and delivering near-real-time data updates for modern platforms. By integrating and streamlining data from multiple sources via our proprietary context engine, DES enhances network visibility by providing enhanced authentication events, additional policy information, expanded error descriptions, and advanced RADIUS accounting insights. The Data Enrichment Service from SecureW2 complements our offerings to ensure a comprehensive network management and security approach.
Enhancing RADIUS Accounting with Cloud RADIUS and Best Practices
Adopting RADIUS Accounting best practices is crucial for organizations seeking to ensure network operations’ precision, security, and efficacy. In this blog post, we have examined the significance of various RADIUS Accounting-related aspects and identified the key steps and practices that can contribute to enhanced accounting processes.
Cloud RADIUS is the next stage in optimizing your network infrastructure. Unlock our innovative cloud-based solution’s scalability, security, and management simplification benefits. Integrating with any Identity Provider (IDP) enables you to experience the efficacy of the administration portal and the seamless authentication process.
Enhance your RADIUS Accounting practices immediately and empower your organization with Cloud RADIUS’ cutting-edge features. Adopt the enumerated best practices to ensure data accuracy, security, and regulation compliance.Contact usto learn how Cloud RADIUS can transform your network operations. Let us help you improve the efficacy and security of your network with our advanced Cloud RADIUS solution.
