Key Points
- SCEP automates certificate management for managed device in an MDM. With an API key and a shared secret, users can sel-enroll themselves for a certificate without the need for manual intervention.
- Static SCEP API key can be intercepted by a hacker. Once a hacker gets the API key, they can manipulate the CA request for a malicious certificate.
- Dynamic SCEP produces a different challenge API key everytime a request is made, thus preventing MITM attacks for added security
Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP) streamlines secure certificate issuance across networked devices, enabling scalable authentication and encryption. Instead of relying on manual provisioning, SCEP automates the process, allowing devices to request certificates directly from the Certificate Authority (CA) through a secure protocol. Devices without valid certificates are denied network access, ensuring only trusted devices can connect.
Microsoft Intune and Jamf leverage SCEP to manage certificates for devices, routers, switches, and applications, delivering a secure and seamless network experience. By deploying SCEP, organizations can eliminate the risks of misconfigured certificates and automate certificate management, reducing operational overhead and strengthening network security. It’s a proven way to enforce secure connections while saving time and resources.
What Is SCEP?
SCEP is a widely used protocol that automates certificate issuance, making it scalable and secure for large environments. SCEP follows the HTTP request and response model and uses RSA cryptography for key management and secure communication. It employs a challenge password in the Certificate Signing Request (CSR) process to verify the request between the client and the Certificate Authority (CA), ensuring only authorized users or devices can obtain certificates.
How Does SCEP Work?
SCEP simplifies secure certificate issuance by authenticating devices using a URL and a shared secret during enrollment. In an MDM system, the SCEP URL can send a payload to managed devices, enabling them to request and receive client certificates seamlessly.
The shared secret, the challenge password, ensures that only authorized devices can request certificates by securely verifying the request with the Certificate Authority (CA). Once an SCEP gateway is established, the server communicates with the CA, exchanging the shared secret to enable a secure configuration. This setup allows devices to auto-enroll for certificates, and after authentication by the CA, user certificates are deployed directly to the devices.
To leverage SCEP with an MDM, a valid SCEP signing certificate is required. This certificate should be signed by the complete certificate chain, including the Root CA, intermediate CA, and signing certificate. This guarantees a secure, trusted connection for automated certificate management.
Do SCEP Deployments Leave Your Network Unsafe?
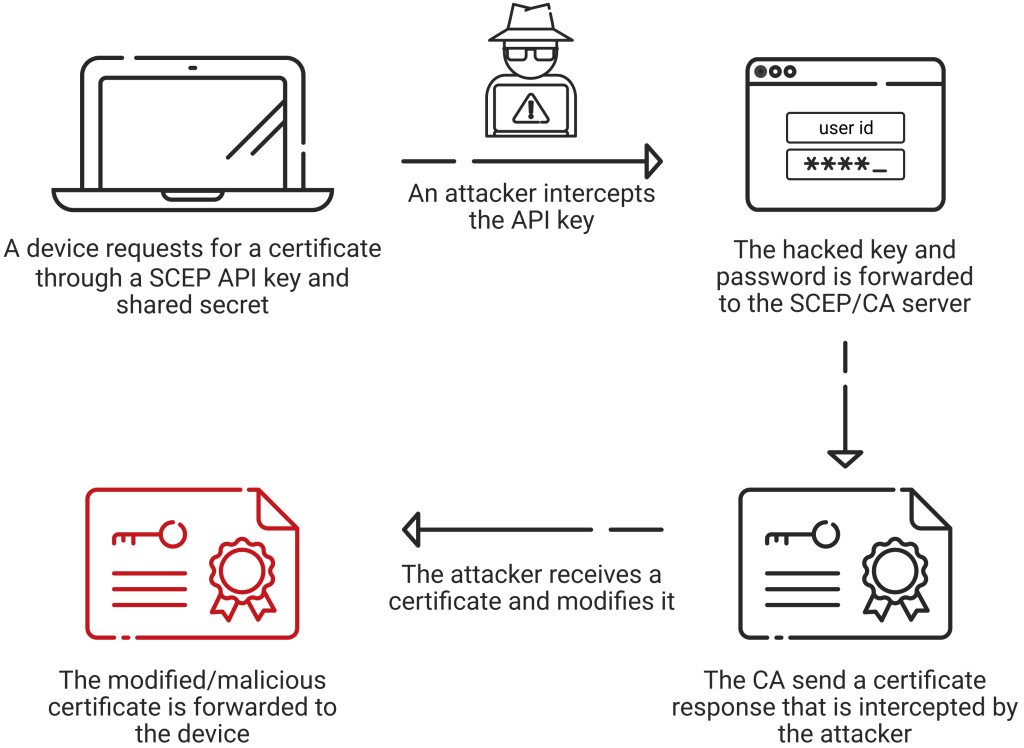
SCEP automates the distribution of certificates to end users in an organizational network, but it does not authenticate or identify the user. If a user has an SCEP challenge password, they can submit a request for a certificate using the same password generated for the organization.
This SCEP model, with a single URL, would work effectively in an admin-only mode. However, SCEP challenge passwords become a concern when used by end users and devices outside the trusted network, such as with MDMs and BYOD scenarios.
This would allow the user or device to take the SCEP challenge password and get a certificate for a different user level with higher network access or a different CA certificate than the intended one. It would also allow an attacker to pose as a legitimate user and use the challenge password to orchestrate attacks on the network.
SCEP Best Practices For A Network Environment
Reusing the same challenge password can make the network vulnerable to unauthorized access by attackers and users. Organizations should follow these best practices when using SCEP:
- Use a separate Intermediate CA for each user group, which provides more security. Intermediate CA’s are hosted from separate locations and help protect the primary CA’s key. If there is a possible attack, it would be contained with an intermediate group rather than affecting the root CA.
- Implement an effective Software Information and Event Management software (SIEM) tool across the organization to collate and manage digital assets. A SIEM tool recreates past events and looks at newer incidents to better monitor malicious and suspicious activities.
- Use ACME instead of SCEP for Apple devices on Jamf, as it provides more secure certificate issuance by using HTTPS to place a CSR.
- Use a Dynamic SCEP Challenge password to configure a dynamic challenge in the profile for a more secure URL instead of a pre-shared key.
What Is Dynamic SCEP?
A dynamic SCEP is a challenge password generated dynamically and assigned to a device by an MDM, like Intune or Jamf. A dynamic SCEP key consists of the following:
- A dynamically generated password that changes every time a new request is placed.
- Parameters that are expected in the CSR.
- The expiry time of the challenge password.
The dynamic SCEP challenge password is signed and encrypted by the MDM. When a device sends a certificate enrollment request, the SCEP server sends the CSR and the encrypted password to the MDM for validation. Upon successful verification, the device can enroll certificates for network access.
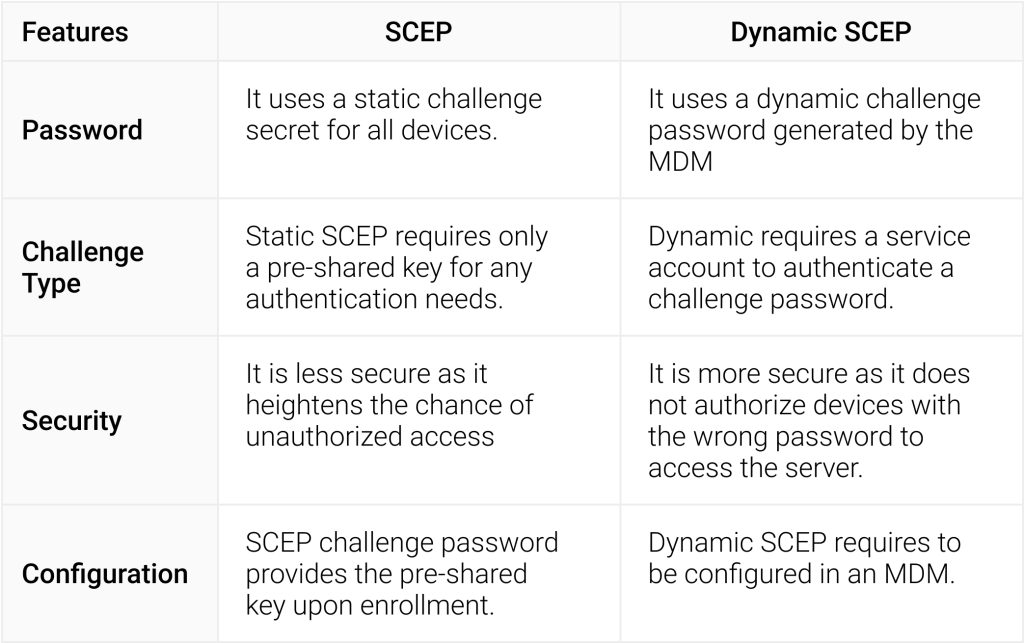
Dynamic SCEP vs SCEP
A dynamic SCEP challenge enhances security by producing a different SCEP challenge key instead of a static one every time. This prevents the misuse of passwords and ensures that only trusted devices and authorized users can authenticate themselves to a network.
Deploy SCEP With SecureW2 For A More Secure Network
An organization must have a scalable and usable certificate distribution system to successfully deploy certificate-based authentication in a network environment. SecureW2’s Managed Gateway API uses SCEP to deploy certificate-based authentication with EAP-TLS in a WPA2-Enterprise network environment for secure, passwordless authentication.
SecureW2 works with an Intune CA partner to create an Identity Provider (IDP) in our JoinNow management portal to help communicate with Intune. An identity provider supplies the endpoint URL to be added to the SCEP profile in Intune. The Certificate Authority (CA) is used here to configure the SCEP process.
Jamf is SecureW2’s preferred Technology Partner, and they have excellent SCEP support and are widely used across the industry. SecureW2 also provides auto revocation of certificates through SCEP on Intune and JAMF, thus minimizing the admin’s effort to revoke expired certificates manually.
Click here to learn more about building a scalable certificate-based network.